Professional Market Analysis Using the A/D Indicator: Key Points Every Trader Should Know
Professional and novice investors understand the crucial role of analytical tools in financial markets. The Accumulation/Distribution (A/D) indicator is one such critical tool, helping investors gain a deeper understanding of market movements. This indicator analyzes the flow of money into and out of stocks and is considered a core component in technical analysis.
The A/D indicator provides insights into the accumulation (buying) and distribution (selling) of capital in the market, allowing investors to make more informed decisions based on the market’s help identify a stock’s strengths and weaknesses. It also signals when it might be a good time to enter or exit an investment.
Investors should be familiar with basic concepts like trading volume and stock closing prices to use the A/D indicator effectively. Analysts use this indicator to track changes in trading volume and their effect on stock prices, helping them identify both long-term and short-term market trends.
Proper education and application of the A/D indicator can significantly improve investment outcomes. Understanding how the A/D indicator reflects actual money flow in the market can help investors select high-potential growth stocks and reduce risk in their investments. Therefore, learning and applying this analytical tool is vital to success and sustainability in financial markets.
A/D Indicator as a Practical Analytical Tool
The A/D indicator, developed by Marc Chaikin, is a highly practical tool for evaluating the inflows and outflows of money in stocks. It focuses on two key components—price and volume—to help investors better understand market dynamics.
The terms “Accumu” ati” n” and” “ist” i “uti” ref” r” to “the tw” main parts of the A/D indicator. It tracks asset accumulation or distribution changes by analyzing price and trading volume. Essentially, this indicator allows investors to make more precise predictions about whether a stock will rise or fall.
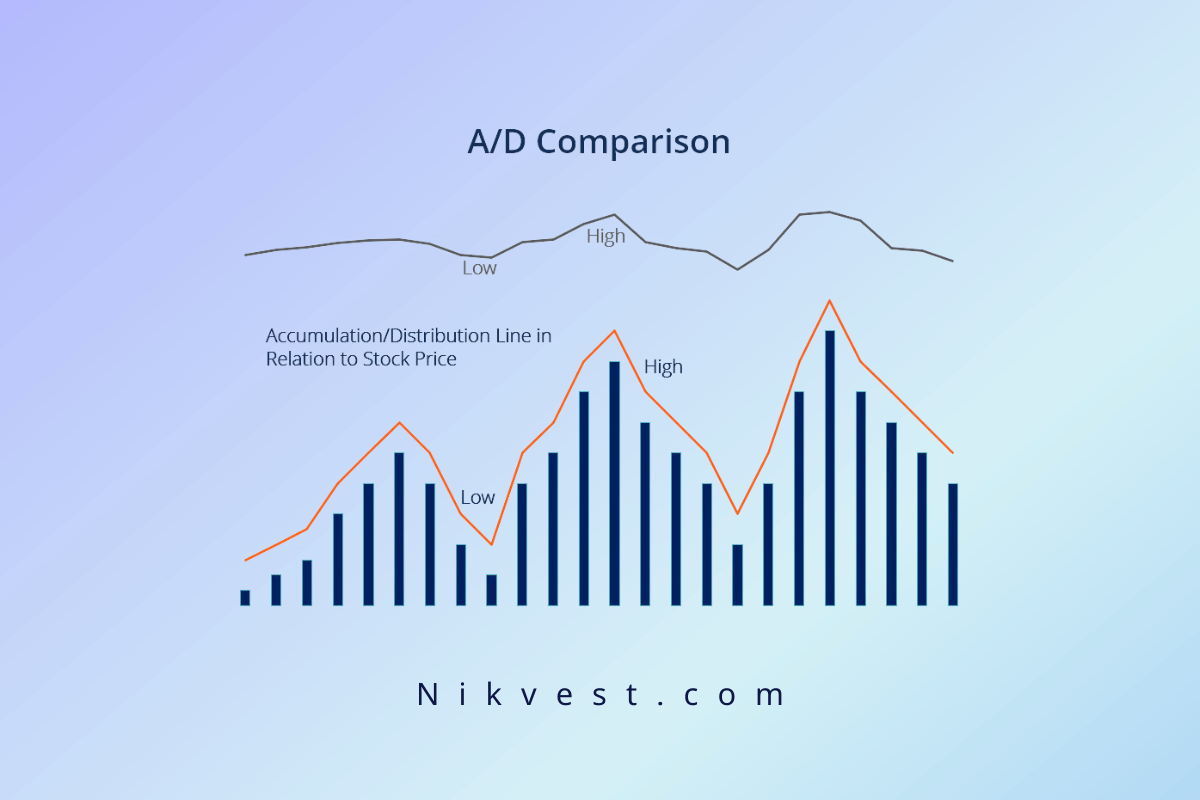
This indicator is commonly used to detect whether money flows into or out of a stock. When the A/D indicator shows accumulation, it means that there is a stronger interest in buying, which could push prices up. On the other hand, when it indicates distribution, it suggests that capital is leaving the stock, potentially causing prices to fall.
Volume is key in this indicator. If a large trading volume accompanies a stock’s stock, the A/D indicator will increase significantly. Conversely, with low volume, the changes in the A/D indicator will be smaller. Ultimately, this indicator is a powerful tool for analyzing market trends and helping investors make more informed decisions.
Analyzing the A/D Indicator
The A/D indicator helps investors understand how supply and demand affect stock prices. It can move in the same direction as the price or in the opposite direction. In volatile markets, especially cryptocurrency markets, mastering the A/D indicator can be a key factor for success.
The A/D indicator calculates a period’period’st and lowest prices and multiplies those values by the trading volume. This process allows investors to monitor the correlation between price changes and trading volume precisely.
The analysis of the A/D indicator is based on changes in trading volume and their effect on stock prices. For example, if the stock price declines and the A/D line slows downward, it indicates a continuation of falling prices.
Interestingly, if the price decreases after an upward trend but the A/D line continues to rise, this could be a sign that prices will soon resume their upward trend. Generally, when prices change direction, but the A/D line remains unchanged, it often signals a possible return to the previous price trend.
However, education and application of the A/D indicator must be only part of a successful investment strategy. The best results come when this indicator is combined with other analytical tools to provide a more comprehensive market view.
Advantages of the A/D Indicator
The Accumulation/Distribution (A/D) indicator offers several significant advantages for investors, making it an essential tool in stock market education and financial market analysis. Here are some of its unique features and benefits:
- Tracking Overall Money Flow: The A/D indicator precisely measures money flow in the market. When the A/D line rises, it signals increased buying pressure and investor interest. Conversely, when the A/D line falls, it indicates rising selling pressure, suggesting that investors are offloading their shares.
- Confirming Market Strength: In addition to tracking money flow, the A/D indicator confirms the strength of the current market trend. It helps investors make more informed decisions based on the strength or weakness of price movements, supporting the analysis of whether a trend is strong or likely to reverse.
- Predicting Potential Market Reversals: The A/D indicator can be used to predict potential changes in market trends. For example, if the A/D line rises while the stock price falls, this could be a sign that prices may soon reverse and resume an upward trend.
- Assisting in Investment Decisions: The A/D indicator helps investors base their investment decisions on solid data and analysis. By offering accurate information about money flow and market strength, it is a reliable guide for buying or selling stocks.
In summary, the A/D indicator plays a crucial role in improving the accuracy and efficiency of investments by providing valuable insights into market trends and money flows.
Disadvantages of the A/D Indicator
Despite its usefulness, the A/D indicator has several limitations that investors should be aware of:
- Ignoring Price Gaps: One key challenge with the A/D indicator is its inability to account for price gaps. Since the indicator is calculated based on a stock’s closing price, it mastock’ssignificant price gaps that occur during the trading day. This can result in inaccuracies, especially when the closing price falls in the middle of an upward or downward trend.
- Difficulty Detecting Small Changes: The A/D indicator sometimes struggles to detect small changes in trading volume. For instance, the price may change slightly in a downtrend, but unless the A/D line rises significantly, it can be difficult to identify the shift.
- Overlooking Periodic Price Changes: Another limitation of the A/D indicator is that it doesn’t accdoesn’tr price chdoesn’teaccdoesn’trrent periods. The indicator focuses only on the stock’s closing price for a stock’seriod, which can cause inconsistencies or irregularities in the chart if there are significant price movements throughout the day.
These limitations highlight that, while the A/D indicator is a powerful market analysis tool, the best results are achieved when combined with other analytical tools. Understanding these constraints helps investors use the A/D indicator more effectively and within a broader context.
Calculation and Formula of the A/D Indicator
To gain a deeper and more precise understanding of the Accumulation/Distribution (A/D) indicator, it is essential to understand its formula and how it is calculated. The A/D indicator uses specific calculations to analyze the financial flows in the market. Follow these steps to calculate the A/D indicator:
1. Calculate the Money Flow Multiplier (MFM)
First, you need to calculate the Money Flow Multiplier (MFM), which shows the impact of closing prices, the lowest, and the highest prices during a given period. The MFM is calculated as follows:
MFM=(Close–Low)–(High–Close)(High–Low)MFM = \frac{(Close – Low) – (High – Close)}{(High – Low)}MFM=(High–Low)(Close–Low)–(High–Close)
Where:
- Close = Closing price of the period.
- Low = Lowest price of the period.
- High = Highest price of the period.
The MFM value ranges between -1 and 1, indicating whether accumulation (positive value) or distribution (negative value) is occurring.
2. Calculate the Money Flow Volume (MFV)
Next, calculate the Money Flow Volume (MFV) using the following formula:
MFV=Volume×MFMMFV = Volume \times MFMMFV=Volume×MFM
Where Volume represents the trading volume for that period.
3. Calculate the Accumulation/Distribution (A/D) Line
Finally, calculate the A/D line using this formula:
A/D=A/Dprevious+MFVA/D = A/D_{previous} + MFVA/D=A/Dprevious+MFV
Where:
- A/D_previous is the A/D value from the previous period.
- MFV is the Money Flow Volume calculated for the current period.
4. Repeat the Process for Each Time Period
At the end of each trading period, the new MFV is added or subtracted from the previous A/D value. This process is continuously repeated, allowing for an accurate calculation of the A/D indicator over time.
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the A/D indicator and utilize it in your financial analyses. This process helps you track money flows and market changes with greater precision, offering valuable insights for trading and investment strategy decision-making.
Signal Generation Using the A/D Indicator

Understanding its signal generation is crucial to effectively use the Accumulation/Distribution (A/D) indicator in market analysis. The A/D indicator typically produces signals in two main categories: bullish (uptrend) and bearish (downtrend). Knowledge of these signals, which can be gained through forex and financial market courses, is vital for investors. Below is a breakdown of how to interpret these signals using the A/D indicator:
- Bullish Signal: Bullish signals are generated when an asset’s price chart is in a asset’snd, but the A/D indicator is rising. This signal indicates increased buying pressure and a weakening of sellers, often pointing to a potential reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend.
- Bearish Signal: Bearish signals occur when the A/D indicator decreases, even though the price chart shows an upward movement. This condition reflects rising selling pressure and suggests that prices may drop in the near future.
- Divergence Detection: Detecting bullish or bearish signals requires accurately identifying the asset’s current trend. When asset’sly identifying bullish or bearish divergences, waiting for confirmation before acting is recommended. In downtrend patterns, pay attention to signals that appear flat or lack clear divergence, which could indicate a lack of significant future changes.
Understanding these signals and applying the A/D indicator correctly helps investors make more informed investment decisions and identify optimal trading opportunities.
A/D Indicator Settings
Understanding the A/D indicator’s settings is esseindicator’stimizing its use in MetaTrader. When you add the A/D indicator to your price chart in MetaTrader, a new window will appear displaying the indicator’s settings. At thiindicator’su have the opportunity to customize the indicator’s appearance, suchindicator’sg the color of the oscillator based on your preferences.
Once you have made your desired adjustments, simply click the OK button to apply the new settings and add the indicator to your price chart. This feature allows the A/D indicator to be displayed in an easy-to-interpret and analyze way. If you ever need to revert the settings to their original state, you can use the Reset button to restore the default settings.
This flexibility in the A/D indicator’sindicator’snablesindicator’sindicator’snablesn market analysis, providing the most efficient data display for your trading strategy. Customizing these settings helps you interpret the indicator’s needs and strategies.
Difference Between the Accumulation/Distribution (A/D) Indicator and the On-Balance-Volume (OBV) Indicator
When discussing financial indicators, a common question arises about the difference between the Accumulation/Distribution (A/D) and the On-Balance-Volume (OBV) indicators. While both indicators rely on volume and price data, there are fundamental differences between them.
The similarity between the A/D and OBV indicators lies in their use of volume and price to analyze market behavior. However, the key differences emerge in how they interpret and process this information:
- OBV Indicator: The OBV indicator primarily focuses on whether a stock’s current closing pricstock’sgher or lower than its previous closing price. If the current closing price is higher, the trading volume for that period is added to the OBV. If it’s lower, its volume is suit’scted. This means that OBV is centered on comparing the stock’s curstock’sice to itsstock’sucurstock’sicece to track the overall flow of capital.
- A/D Indicator: In contrast, the A/D indicator operates differently. It does not consider the previous closing price in its calculations. Instead, it uses a specific multiplier based on where the closing price is located relative to the stock’s higstock’sow prices stock’sahigstock’sowriod. This method allows A/D to measure how accumulation (buying) or distribution (selling) affects the stock’s pristock’sin that tistock’sepristock’sination Difference:
- OBV focuses on price changes to track money flow from one period to the next.
- A/D evaluates the position of the closing price within the period’s high-low range, givperiod’sght into whether there is more asset accumulation or distribution in the market.
As a result, the signals generated by each indicator differ:
- OBV is more concerned with overall money flow in or out of an asset.
- A/D provides insight into how money is being accumulated or distributed over time.
Both tools can be useful in different analytical strategies and offer valuable insights to traders, helping them make informed decisions based on the flow of capital and market dynamics.
In Conclusion
Learning and applying the A/D (Accumulation/Distribution) indicator, a powerful tool in technical analysis can greatly assist investors in identifying and analyzing trading opportunities in financial markets. Based on two key components—volume and price—this indicator provides useful signals that help predict future price trends.
One of the most important uses of the A/D indicator is its ability to detect the accumulation or distribution of assets. By analyzing changes in price and volume, it allows investors to understand significant market movements better. Furthermore, using the A/D indicator alongside other analytical tools can enhance the identification of optimal stocks and help determine the right times for buying and selling.
The A/D indicator, with its reliance on volume and price, is a comprehensive and valuable tool for market analysts. It helps analysts better understand money flows and asset movements within the market and is also effective in predicting both long-term and short-term market trends. Therefore, learning how to use the A/D indicator in combination with other tools can lead to smarter decision-making and greater success in trading.