50-Day Moving Average Strategy
In the vast and complex world of trading and investing, mastering market trends is crucial for making informed decisions. One of the most effective and widely-used tools in technical analysis is the moving average. Specifically, the 50-day moving average (50-DMA) has proven to be a powerful indicator for traders and investors alike. This strategy is simple, yet when used effectively, it can help in identifying trends, optimizing entries and exits, and managing risk. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the 50-day moving average strategy, how to use it, and its advantages and limitations.
What is a 50-Day Moving Average?
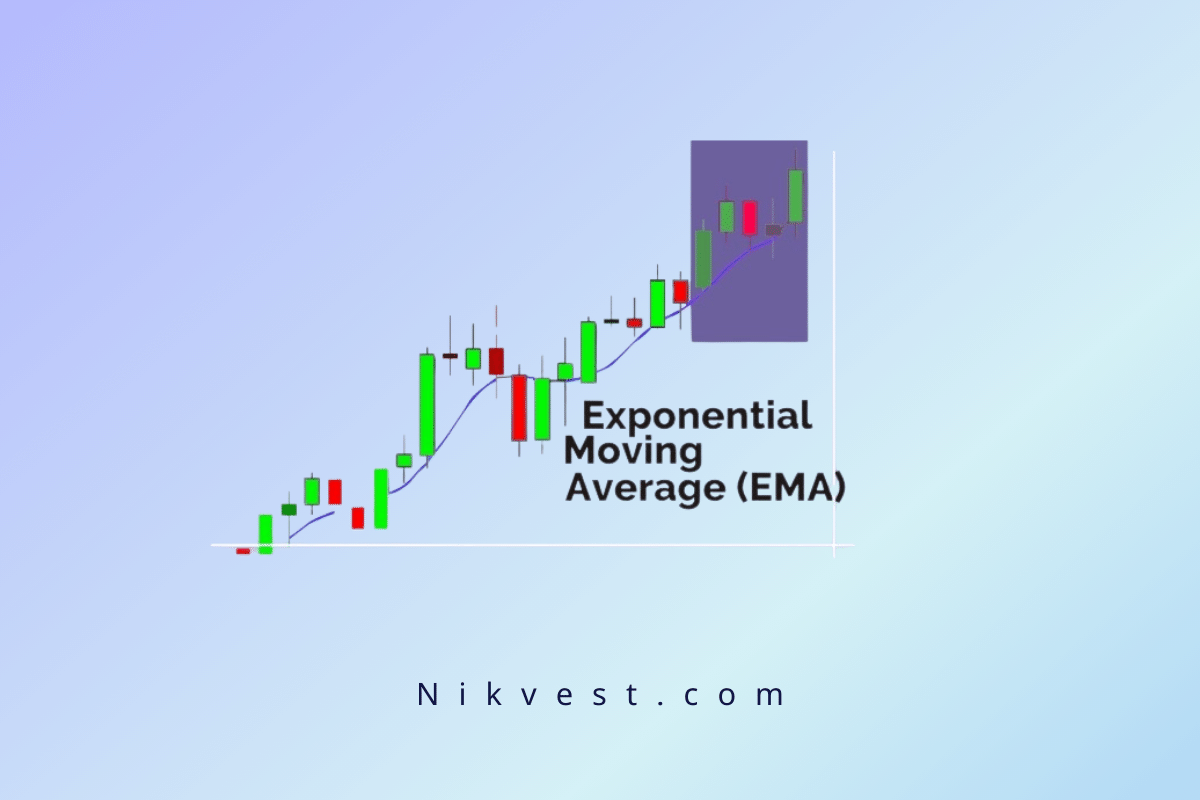
A 50-day moving average is a trend-following indicator that calculates the average closing price of an asset over the last 50 days. By plotting this average on a price chart, traders can smooth out the day-to-day price fluctuations and get a clearer picture of the overall trend. It’s considered a medium-term indicator and is widely used because it strikes a balance between short-term noise and long-term trends.
There are two primary types of 50-day moving averages:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): The average price of the asset over the last 50 days.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Similar to SMA, but it gives more weight to recent price data, making it more responsive to current market conditions.
The 50-DMA is often plotted on price charts as a line, and traders use it as a reference to make decisions on buying or selling.
How is the 50-Day Moving Average Calculated?
The calculation of a simple moving average (SMA) is straightforward:
- Take the closing prices of the asset over the past 50 trading days.
- Add them up.
- Divide the total by 50.
This results in the 50-day simple moving average.
For example, if the closing prices of a stock over the last 50 days total $5,000, the 50-DMA would be:
50-DMA = 5000/50 = 100
Thus, the average price over the last 50 days is $100. This smooths out any day-to-day fluctuations and gives traders a clearer view of the trend.
The exponential moving average (EMA) calculation is more complex, as it places more weight on recent prices. This makes the EMA more sensitive to recent price movements, which can be beneficial for traders who want quicker signals.
Why the 50-Day Moving Average?
The 50-day moving average is widely used for several reasons:
-
Medium-Term Trend Indicator
The 50-day moving average is perfect for traders looking to capture medium-term trends. It’s not as short as a 20-day moving average, which can generate too many signals, nor is it as long as the 200-day moving average, which might react too slowly to changes in market conditions. As a result, the 50-DMA provides a balanced view of the market.
-
Widely Followed by Traders
Because of its popularity, the 50-DMA can serve as a self-fulfilling prophecy. Many traders watch for price actions around the 50-DMA, leading to increased buying or selling when price levels interact with this line. This can amplify the reliability of the 50-DMA as a support or resistance level.
-
Clear Trend Indicator
The 50-DMA helps identify the prevailing trend. If the price is above the 50-DMA, it generally signals an uptrend, while prices below it indicate a downtrend. This clear visual helps traders make decisions in line with the trend, which is a cornerstone of successful trading.
Basic 50-Day Moving Average Strategy
Now that we know what the 50-day moving average is and why it’s used, let’s dive into the basic strategy for using it.
-
Crossover Strategy
One of the most popular uses of the 50-DMA is the crossover strategy, which involves looking for the point where the price crosses the moving average.
– Buy Signal: When the price crosses above the 50-DMA, it is typically seen as a bullish signal, indicating that the asset’s price is gaining momentum. Traders may enter a long position or buy the asset.
– Sell Signal: When the price crosses below the 50-DMA, it is seen as a bearish signal, suggesting that the price is losing momentum. Traders may close long positions or consider shorting the asset.
-
Support and Resistance
The 50-DMA often acts as dynamic support and resistance. In an uptrend, the price may pull back to the 50-DMA, where it finds support and continues higher. In a downtrend, the 50-DMA may act as resistance, where the price struggles to move above it.
Advanced 50-Day Moving Average Strategies
While the basic crossover and support/resistance strategies are effective, more advanced traders combine the 50-DMA with other indicators for even more precise signals.
-
50-DMA and 200-DMA: The Golden Cross and Death Cross
When combined with the 200-day moving average, the 50-DMA forms the foundation for two highly regarded signals:
– Golden Cross: When the 50-DMA crosses above the 200-DMA, it forms a Golden Cross, signaling a long-term bullish trend. This is often considered a strong buy signal.
– Death Cross: When the 50-DMA crosses below the 200-DMA, it forms a Death Cross, which signals a long-term bearish trend. Traders may take this as a signal to sell or short the asset.
These signals are particularly popular in stock markets, where they can signal major shifts in long-term market trends.
-
50-DMA and Volume Confirmation
Volume is a critical factor in confirming the reliability of moving average signals. For example:
– Price crossing above the 50-DMA on high volume: This is a stronger signal that the trend may continue higher, as it shows that there is significant buying interest.
– Price crossing below the 50-DMA on low volume: This could indicate that the downtrend lacks conviction and might reverse soon.
Traders can use volume to filter out false signals and increase the accuracy of their trades.
-
Combining 50-DMA with RSI
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a momentum oscillator that measures whether an asset is overbought or oversold. When used in conjunction with the 50-DMA, it can provide even stronger trading signals.
– Buy Signal: If the price crosses above the 50-DMA and the RSI is below 30 (oversold), it’s a strong indication that the asset may reverse upward.
– Sell Signal: If the price crosses below the 50-DMA and the RSI is above 70 (overbought), it may signal an upcoming price drop.
Strengths of the 50-Day Moving Average Strategy
Like any technical indicator, the 50-DMA strategy has its strengths and weaknesses. Let’s begin with the strengths:
-
Simple and Easy to Use
One of the greatest strengths of the 50-DMA strategy is its simplicity. Traders don’t need to know complex algorithms or calculations to use it effectively. The moving average can be quickly added to any charting software, and its signals are easy to interpret.
-
Effective Trend Indicator
The 50-DMA is excellent at identifying trends. While no indicator can predict the market with 100% accuracy, the 50-DMA does a good job of highlighting the general direction of the market, allowing traders to enter positions that align with the prevailing trend.
-
Works in Different Markets
The 50-DMA can be used across multiple markets, including stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. This versatility makes it a valuable tool for traders in any asset class.
Limitations of the 50-Day Moving Average Strategy
While the 50-DMA has many strengths, it’s important to be aware of its limitations:
-
Lagging Indicator
One of the key criticisms of moving averages, including the 50-DMA, is that they are lagging indicators. Because the 50-DMA is based on past price data, it reacts slower to real-time market changes. As a result, traders using this strategy may enter or exit trades later than desired, potentially missing out on optimal entry or exit points.
-
False Signals in Choppy Markets
In a sideways or range-bound market, the price may cross above and below the 50-DMA multiple times, generating false signals. Traders may get caught in a series of whipsaw trades, leading to losses. This is why combining the 50-DMA with other indicators, such as volume or the RSI, can help avoid false signals.
-
Not Suitable for Short-Term Trading
The 50-DMA is not well-suited for short-term traders, such as day traders or scalpers, who rely on more responsive indicators. The 50-DMA focuses on the medium-term trend and may be too slow to react to quick market changes that short-term traders look to exploit.
How to Backtest the 50-Day Moving Average Strategy
Before applying any strategy in live markets, it’s essential to backtest it using historical data. Back testing allows traders to understand how the strategy would have performed in past market conditions and refine their approach before risking real capital. Here’s how you can backtest the 50-day moving average strategy:
Step 1: Choose Your Asset and Time Frame
First, select the asset you want to test (such as stocks, forex, commodities, or cryptocurrencies) and the time frame (daily, weekly, or monthly). Since the 50-DMA is a medium-term indicator, it’s typically used on daily or weekly charts, although traders can adapt it to longer or shorter time frames depending on their strategy.
Step 2: Set the Entry and Exit Rules
Define the specific rules for entering and exiting trades. For example:
– Entry Rule: Buy when the price crosses above the 50-DMA.
– Exit Rule: Sell when the price crosses below the 50-DMA.
You can also include additional rules, such as only taking trades where the RSI is oversold or only entering trades when the volume is above the average.
Step 3: Gather Historical Price Data
Using your chosen charting platform (e.g., TradingView, MetaTrader, or ThinkorSwim), gather historical price data for your asset. Most platforms allow you to overlay the 50-day moving average on historical price charts.
Step 4: Manually or Automatically Backtest
You can either manually backtest by visually going through the historical data and marking where the 50-DMA signaled buys and sells, or use automated tools provided by some platforms to backtest the strategy over a longer time frame. Automated backtesting can provide insights into the performance metrics such as win/loss ratio, profit factor, and maximum drawdown.
Step 5: Analyze the Results
Once you’ve backtested the strategy, analyze the results. Pay attention to the following metrics:
– Winning Trades vs. Losing Trades: How many trades were successful?
– Average Profit per Trade: What was the average gain on each successful trade?
– Maximum Drawdown: What was the largest peak-to-trough loss during the test period?
– Profit Factor: This measures the overall profitability by dividing total profits by total losses.
By analyzing these factors, you can determine whether the 50-day moving average strategy is suitable for your trading style and risk tolerance.
Real-World Examples of the 50-Day Moving Average Strategy in Action
To further illustrate the power of the 50-day moving average, let’s look at some real-world examples where the 50-DMA played a crucial role in market movements.
Example 1: Apple Inc. (AAPL)
Apple’s stock has consistently interacted with the 50-DMA over the years, providing traders with clear buy and sell signals. In early 2020, amid the COVID-19 pandemic, Apple’s stock saw significant volatility. After falling below the 50-DMA during the initial market sell-off, it eventually crossed back above the 50-DMA in April 2020, signaling a strong buy opportunity as the stock went on to rally significantly throughout the year.
Many traders who followed this 50-DMA signal were able to capture substantial gains as the stock surged to new all-time highs by the end of 2020.
Example 2: Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin, known for its volatility, has also been closely tied to the 50-day moving average in recent years. During its 2020-2021 bull run, Bitcoin consistently stayed above the 50-DMA, with each pullback to the moving average providing buying opportunities for traders. However, in May 2021, Bitcoin dropped below the 50-DMA, signaling the end of the bull trend and a potential reversal.
Traders who recognized this breakdown were able to exit their long positions or short the cryptocurrency, avoiding significant losses during the subsequent bear market.
Can You Automate the 50-Day Moving Average Strategy?
Yes, you can automate the 50-day moving average strategy using algorithmic trading or trading bots. Many traders choose to automate their strategies to remove emotional biases and improve the speed and accuracy of trade execution. Here’s how automation works with the 50-DMA strategy:
-
Trading Platforms with Automation Capabilities
Most modern trading platforms, such as MetaTrader, NinjaTrader, and Interactive Brokers, offer the ability to automate trading strategies. You can write a script or use pre-built strategies to automate entries and exits based on the 50-DMA. For example, you can program the platform to automatically buy when the price crosses above the 50-DMA and sell when the price crosses below it.
-
Backtesting and Optimization
One of the advantages of automating a strategy is the ability to backtest and optimize it across different time periods and assets. By running historical simulations, traders can refine their parameters, such as adjusting the time frame or combining the 50-DMA with other indicators like RSI or MACD for better results.
-
Benefits of Automation
– No Emotional Trading: Automated systems follow predefined rules without being affected by emotions like fear or greed.
– Speed and Efficiency: Trading bots can monitor multiple assets and execute trades faster than human traders.
– Consistency: Automation ensures that the same strategy is followed consistently without deviating from the plan.
-
Risks of Automation
While automation has its benefits, it’s not without risks. Algorithmic systems can malfunction, leading to missed trades or incorrect executions. Additionally, over-optimizing a strategy based on historical data can result in overfitting, where the strategy performs well in backtests but poorly in live markets.
Frequently Asked Questions About the 50-Day Moving Average Strategy
-
Can the 50-DMA Strategy Be Used in Any Market?
Yes, the 50-DMA strategy can be used in a variety of markets, including stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. However, it’s important to adjust the strategy based on the characteristics of each market. For example, the volatility of cryptocurrencies may require using the exponential moving average (EMA) for quicker reactions to price changes.
-
Is the 50-DMA Suitable for Short-Term Trading?
The 50-DMA is not ideal for short-term trading, such as day trading or scalping, as it focuses on medium-term trends. Short-term traders may prefer using shorter moving averages, like the 20-day or even 10-day moving average, for quicker signals.
-
How Do You Avoid False Signals in a Choppy Market?
False signals are common in sideways or range-bound markets where prices fluctuate around the 50-DMA. To avoid false signals, traders can use additional confirmation indicators, such as the RSI or MACD, or pay attention to trading volume to verify the strength of the trend.
- Should I Use the Simple Moving Average (SMA) or the Exponential Moving Average (EMA)?
The choice between SMA and EMA depends on your trading style. The SMA gives equal weight to all price data, making it more stable and better for filtering out short-term noise. The EMA gives more weight to recent price data, making it more responsive to price changes. Traders looking for quicker signals may prefer the EMA.
Conclusion: Is the 50-Day Moving Average Strategy Right for You?
The 50-day moving average strategy is a time-tested tool that provides traders and investors with a simple yet effective way to identify trends, manage risk, and find trading opportunities. Its versatility allows it to be used across a wide range of markets, from stocks to forex and cryptocurrencies. Whether you’re a beginner looking for a simple trend-following strategy or an experienced trader seeking to enhance your trading plan, the 50-DMA can be a valuable tool in your technical analysis toolkit.
In conclusion, the 50-day moving average strategy is a reliable and easy-to-use indicator that can provide valuable insights into market trends and improve trading performance. With proper backtesting, optimization, and risk management, traders can make the 50-DMA an integral part of their trading strategy and increase their chances of success in the financial market