The 200-Day Moving Average Crossover Strategy
The moving average (MA) crossover strategy is a cornerstone in technical analysis, widely used by both novice and experienced traders to identify trends and determine entry and exit points in the market. The 200-day moving average (200-day MA), in particular, stands out as a powerful tool for assessing long-term market trends. This strategy focuses on the relationship between a shorter-term moving average (such as the 50-day MA) and the 200-day MA, providing clear signals that can help traders make informed decisions.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explain how the 200-day MA crossover strategy works, its benefits, drawbacks, and how it compares to other moving averages like the 20-day and 50-day MAs. Additionally, we’ll explore various ways to enhance this strategy, making it more adaptable to different market conditions.
Understanding Moving Average Crossovers: A Simple Explanation
A moving average (MA) smooths out price data over a specific period, making it easier to identify the overall direction of a market or asset. By calculating the average price over a set number of days, moving averages help traders cut through the noise of short-term price fluctuations and focus on the bigger picture.
In a moving average crossover, two different MAs are plotted on a price chart, typically a shorter-term and a longer-term MA. A crossover occurs when the two MAs intersect. This crossover can signal a change in market momentum:
– When a shorter-term moving average crosses above a longer-term moving average, it’s often interpreted as a bullish signal. This suggests the market is gaining upward momentum and that prices could continue rising.
– Conversely, when a shorter-term moving average crosses below a longer-term moving average, it’s considered a bearish signal, indicating that the market may be losing momentum and entering a downtrend.
The 200-day MA is particularly significant because it reflects a long-term trend, smoothing out price data over nearly a year of trading days. When combined with a shorter-term moving average, such as the 50-day MA, the 200-day MA can reveal potential shifts in market sentiment.
2 Methods for Using MA Crossovers in Trading
There are two main methods for using moving average crossovers in trading: the golden cross and death cross, and the dual moving average crossover system.
-
Golden Cross and Death Cross
The golden cross and death cross are widely recognized patterns that signify major shifts in market momentum. These crossovers involve a shorter-term moving average (usually the 50-day MA) crossing above or below the 200-day MA:
– Golden Cross: This occurs when the 50-day MA crosses above the 200-day MA. It’s a bullish signal that indicates the market could be entering a long-term uptrend. Traders typically see this as an opportunity to buy, anticipating further upward price movement.
– Death Cross: The death cross happens when the 50-day MA crosses below the 200-day MA, signaling a potential downtrend. This bearish signal suggests that prices may continue falling, prompting traders to exit long positions or enter short trades.
Both of these crossovers provide clear, actionable signals for traders looking to capitalize on long-term trends.
-
Dual Moving Average Crossover System
The dual moving average crossover system involves using two moving averages of different lengths, such as the 20-day MA and the 50-day MA, or the 50-day MA and the 200-day MA. Traders use this system to generate buy or sell signals based on the crossover between the two MAs:
– Buy Signal: When the shorter-term moving average crosses above the longer-term moving average, it’s a signal to enter a long position. This suggests that upward momentum is building and that prices may continue to rise.
– Sell Signal: When the shorter-term moving average crosses below the longer-term moving average, it’s a signal to exit a long position or enter a short position. This suggests that downward momentum is strengthening, and prices may continue to fall.
The dual moving average crossover system is versatile and can be applied to various time frames, depending on the trader’s strategy and market conditions.
How to Interpret the 20-Day, 50-Day, and 200-Day Moving Averages
20-Day Moving Average
The 20-day moving average is a short-term trend indicator. It reacts quickly to price changes and is often used by day traders and swing traders to capture short-term movements. A crossover involving the 20-day MA can indicate rapid shifts in momentum, making it suitable for short-term trading strategies.
For instance, when the 20-day MA crosses above a longer-term moving average, it signals a short-term bullish trend. Conversely, when it crosses below, it suggests that short-term bearish sentiment is taking hold.
50-Day Moving Average
The 50-day moving average is considered a medium-term trend indicator. It strikes a balance between short-term volatility and long-term stability, making it popular among swing traders and investors alike. The 50-day MA is especially useful for identifying intermediate market trends and is often used in conjunction with the 200-day MA to generate golden cross and death cross signals.
When the 50-day MA crosses above or below the 200-day MA, it typically indicates a significant change in market sentiment, making it a key indicator for long-term trend analysis.
200-Day Moving Average
The 200-day moving average is a long-term trend indicator. It smooths out price data over approximately 200 trading days (roughly 40 weeks) and is often viewed as a benchmark for the overall health of the market. Many investors and traders use the 200-day MA to identify major trends and assess the market’s long-term direction.
When the price of an asset is above the 200-day MA, it’s generally considered to be in an uptrend, whereas a price below the 200-day MA suggests a downtrend.
200-Day Moving Average Crossover Strategy Overview
The 200-day moving average (MA) crossover strategy is widely regarded as a simple yet powerful method to identify long-term trends and potential buy and sell opportunities in financial markets. It leverages the interaction between a shorter-term moving average (typically the 50-day MA) and the 200-day MA, focusing on significant market movements. The strategy helps traders and investors make more informed decisions by reducing noise from short-term price fluctuations and focusing on the broader market trend.
Key Components of the 200-Day MA Crossover Strategy
-
The 200-Day Moving Average
The 200-day MA is a long-term moving average calculated by averaging an asset’s closing prices over the past 200 trading days. This indicator smooths out price fluctuations over a substantial period, allowing traders to see the overall direction of the market without being influenced by short-term volatility. It acts as a “trend filter,” helping to differentiate between bullish and bearish market conditions. A price above the 200-day MA is generally considered a sign of a healthy, bullish market, while a price below it is seen as a signal of potential weakness or bearish sentiment.
-
Shorter-Term Moving Average (e.g., 50-Day MA)
While the 200-day MA reflects the long-term trend, shorter-term moving averages, like the 50-day MA, react more quickly to price movements. The 50-day MA is the most commonly paired with the 200-day MA in this strategy, offering an intermediate-term perspective. The interaction between the 50-day MA and the 200-day MA generates the crossover signals (golden cross and death cross), which traders use to make decisions.
How the 200-Day MA Crossover Works?
The strategy works by tracking the relationship between the 50-day MA and the 200-day MA to generate buy or sell signals. It produces two primary crossover signals that traders use to enter or exit the market:
-
Golden Cross (Bullish Signal)
A golden cross occurs when the 50-day MA crosses above the 200-day MA. This crossover is widely regarded as a bullish signal, indicating the potential beginning of an upward trend. When this happens, it suggests that recent price momentum is positive, and the short-term trend is strong enough to push the asset’s price above its long-term average. This is often seen as a buy signal, prompting traders to enter long positions in anticipation of further price gains.
The golden cross is significant because it shows a shift in market sentiment from bearish to bullish, especially if it is accompanied by increasing trading volume. The higher volume reinforces the idea that more market participants are aligning with the upward momentum, increasing the likelihood of a sustained rally.
-
Death Cross (Bearish Signal)
A death cross occurs when the 50-day MA crosses below the 200-day MA. This is considered a bearish signal, indicating that the asset may be entering a long-term downtrend. The death cross suggests that short-term price momentum has weakened to the point where the asset’s price falls below its long-term average, which could lead to further declines. Traders typically see this as a sell signal, and many exit long positions or open short positions to take advantage of the anticipated downward movement.
The death cross is considered particularly powerful because it highlights a shift in market sentiment from bullish to bearish. If accompanied by a reduction in trading volume or other bearish technical indicators, it can signal that a major downtrend is beginning, providing traders with an opportunity to protect their capital or profit from falling prices.
How to Implement the 200-Day MA Crossover Strategy?
Implementing the 200-day MA crossover strategy is straightforward and involves a few basic steps:
-
Set Up the Chart
Start by plotting both the 50-day and 200-day moving averages on your chart. Most trading platforms allow traders to apply moving averages with customizable time periods easily. You can use daily charts for long-term trading or adjust the time frame depending on your preferred trading style (for example, weekly or hourly charts for shorter-term trading).
-
Identify the Crossover Points
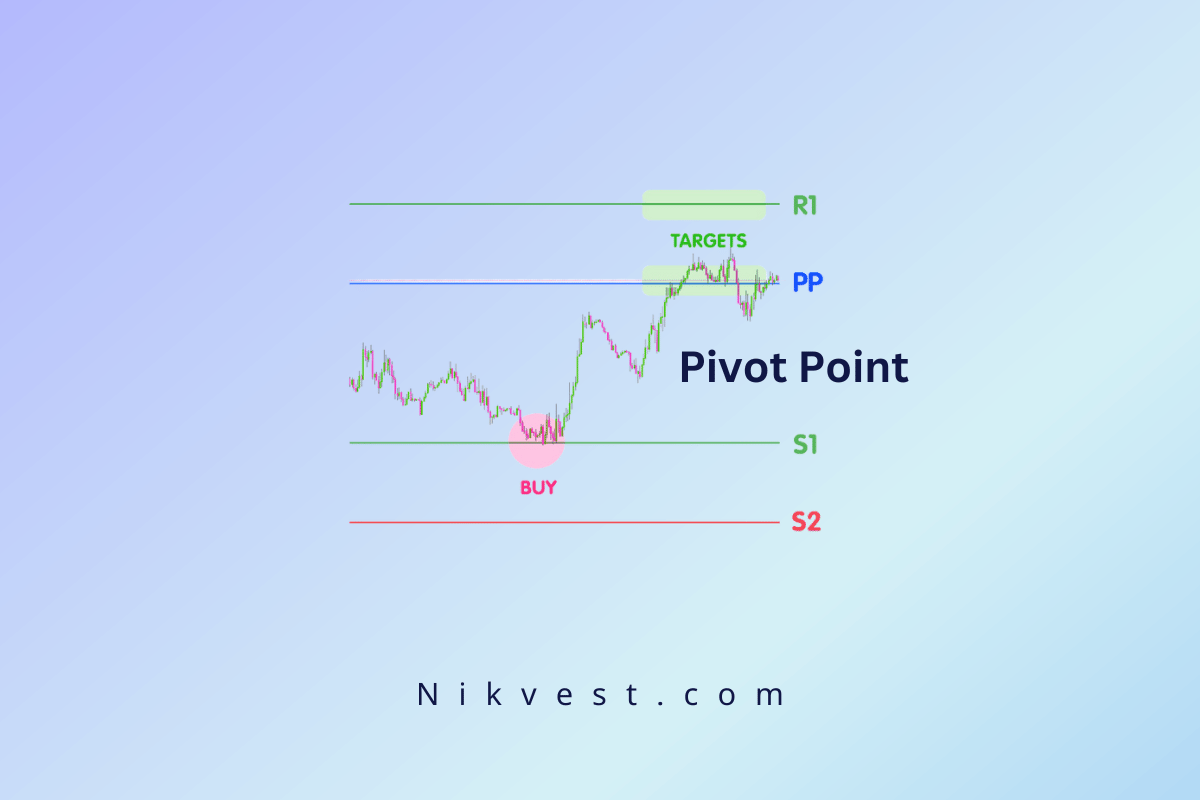
Monitor the interaction between the 50-day and 200-day MAs. The key is to watch for crossover points where the two lines intersect, which serve as your buy or sell signals. A golden cross (50-day crossing above the 200-day) is a buy signal, while a death cross (50-day crossing below the 200-day) is a sell signal.
-
Confirm with Other Indicators
While the crossover signals are useful, many traders enhance the strategy by confirming the signals with other technical indicators. Tools like the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), and support/resistance levels can help filter out false signals and improve the accuracy of trades.
-
Enter or Exit the Trade
Once you’ve identified a valid crossover and confirmed it with additional indicators, you can enter a trade. For a golden cross, you would typically enter a long position, expecting prices to rise. For a death cross, you may either close your long positions or enter short positions, expecting prices to fall.
- Risk Management
Risk management is crucial when using the 200-day MA crossover strategy. Traders should always set stop-loss levels to protect themselves in case the trade goes against them. Since the strategy is based on long-term trends, large price swings can occur, and stop-losses help mitigate potential losses if the trend reversal fails.
Why the 200-Day MA is Important?
The 200-day MA is widely followed by institutional investors, hedge funds, and retail traders, making it a self-fulfilling indicator in many ways. It acts as a psychological benchmark, reflecting the collective sentiment of market participants:
– Institutional Impact: Many institutional investors base their decisions on the 200-day MA. A price consistently above the 200-day MA often attracts large-scale buying from institutions, while a price below it might lead to increased selling. The collective influence of institutional investors reacting to these signals can significantly impact the market’s direction.
– Psychological Benchmark: The 200-day MA is also a psychological indicator for individual traders. It’s often considered a “line in the sand,” separating bullish from bearish market sentiment. If the price of an asset is trading above the 200-day MA, many traders view it as a sign that the market is healthy. When it falls below the 200-day MA, there’s often concern that the market may be weakening, triggering a shift in sentiment.
Example of the 200-Day MA Crossover in Action
Imagine a stock has been trading in a downtrend for several months, with its price consistently below the 200-day MA. Over time, the price starts to stabilize and moves higher, causing the 50-day MA to approach the 200-day MA. Eventually, the 50-day MA crosses above the 200-day MA, forming a golden cross. This signals that the stock may have entered a new uptrend.
Traders who are monitoring this crossover could interpret it as a buy signal, particularly if the crossover is confirmed by other indicators like increasing volume or bullish divergence in the RSI or MACD. They might enter a long position, expecting the stock to continue rising. Over the following weeks, the stock’s price climbs, and the trader remains in the trade, benefiting from the upward trend.
On the flip side, when the same stock starts losing momentum, the 50-day MA could start to decline toward the 200-day MA. When it crosses below the 200-day MA, it forms a death cross, signaling a potential trend reversal. Traders might interpret this as a sell signal, and those holding long positions might exit to lock in profits or prevent further losses.
Flexibility of the Strategy Across Markets
The 200-day MA crossover strategy is highly versatile and can be applied to various financial markets, including:
– Stocks: The 200-day MA crossover is most commonly used in the stock market to identify trends in individual equities or broader indices (like the S&P 500).
– Commodities: Traders in the commodities market can use this strategy to track trends in assets like gold, oil, and agricultural products.
– Forex: In currency markets, the 200-day MA crossover strategy can be used to identify long-term trends in major currency pairs (e.g., EUR/USD, USD/JPY)
– Cryptocurrencies: As the cryptocurrency market matures, traders increasingly apply the 200-day MA crossover strategy to digital assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum to identify major bullish or bearish trends.
When to Use the 200-Day MA Crossover Strategy
The 200-day MA crossover strategy is best suited for trending markets, where prices are moving consistently in one direction. It’s less effective in sideways or choppy markets, where prices fluctuate without establishing a clear trend. In such environments, traders may experience multiple false crossovers, leading to whipsaws—frequent trades that result in minimal gains or losses.
However, in trending markets, the 200-day MA crossover strategy can provide highly reliable signals. By focusing on the long-term trend and using additional indicators for confirmation, traders can increase their chances of making profitable trades.
The 200-day moving average crossover strategy is one of the most reliable tools for identifying long-term trends and generating actionable buy or sell signals. Its simplicity, coupled with its ability to filter out short-term noise, makes it a favorite among traders and investors alike. While the strategy is not without its drawbacks—such as lagging signals and potential false crossovers in choppy markets—when used correctly and with additional confirmation from other indicators, it can be highly effective.
By understanding the mechanics of the 200-day MA crossover and applying it with discipline, traders can position themselves to capitalize on significant market movements, benefiting from the collective market sentiment that often accompanies these major crossover signals.
Benefits of Using the MA Crossover Strategy
The 200-day moving average crossover strategy offers several key benefits for traders and investors:
-
Clear Trend Identification
The MA crossover strategy provides a straightforward way to identify trends. By focusing on the relationship between short-term and long-term moving averages, traders can easily spot when market sentiment is shifting. This allows them to enter or exit trades at optimal times, capitalizing on major market movements.
-
Simplicity
One of the main advantages of the MA crossover strategy is its simplicity. Traders don’t need to rely on complex indicators or elaborate calculations. The crossover points between two moving averages provide clear, objective signals that can be easily understood and acted upon.
-
Long-Term Focus
The 200-day MA crossover strategy is particularly well-suited for long-term investors. By focusing on the 200-day MA, traders can avoid the noise of short-term price fluctuations and concentrate on the overall direction of the market. This helps to reduce the risk of making impulsive trading decisions based on short-term volatility.
-
Objective Signals
The crossover strategy provides objective, data-driven signals that reduce the impact of emotions on trading decisions. This helps traders maintain discipline and avoid the psychological pitfalls of fear and greed, which can often lead to poor trading decisions.
Drawbacks of the MA Crossover Strategy
Despite its many advantages, the MA crossover strategy also has some notable drawbacks:
-
Lagging Indicator
Moving averages are lagging indicators, meaning that they rely on historical price data. As a result, crossover signals often occur after a trend has already started, which means traders may miss the initial move. This can lead to late entries or exits, reducing the potential profit from a trade.
-
False Signals in Choppy Markets
In sideways or choppy markets, moving average crossovers can generate false signals. This occurs when the moving averages frequently cross and uncross, leading to whipsaws—a situation in which traders enter and exit trades based on insignificant price movements. This can result in a series of unprofitable trades and frustration for traders.
-
Limited Effectiveness in Ranging Markets
The MA crossover strategy works best in trending markets, where prices are moving steadily in one direction. In ranging or sideways markets, where prices fluctuate within a narrow range, moving averages may not provide reliable signals. Traders using this strategy in such conditions may experience multiple false crossovers, leading to poor trading decisions.
-
Not Suitable for Short-Term Trading
The 200-day moving average crossover strategy is designed for long-term trend analysis. As such, it’s not ideal for short-term traders who need faster, more responsive signals. Short-term traders, such as day traders or swing traders, might find the 200-day MA too slow to react to quick market movements. For those traders, shorter moving averages like the 20-day or 50-day MA might be more suitable for capturing short-term trends.
Pros and Cons of the 200-Day MA Crossover Strategy
To provide a clearer perspective, here’s a breakdown of the pros and cons of the 200-day MA crossover strategy:
Pros:
- Long-Term Trend Identification:
The 200-day MA is an excellent tool for identifying long-term trends. This makes it useful for investors with a longer time horizon, helping them avoid getting caught up in the day-to-day market noise.
- Strong Signals:
The golden cross and death cross signals generated by the 200-day MA crossover are widely recognized and followed by traders and investors alike. These signals often reflect significant shifts in market sentiment, making them reliable indicators for major market moves.
- Simplicity:
The 200-day MA crossover strategy is easy to understand and implement, even for beginner traders. The crossover points between the shorter and longer-term MAs provide clear buy and sell signals, making the strategy accessible to a broad range of traders.
- Reduces Market Noise:
By focusing on long-term trends, the 200-day MA filters out short-term price volatility. This helps traders maintain a long-term perspective and reduces the likelihood of making impulsive decisions based on minor price fluctuations.
- Applicable to Various Markets:
The 200-day MA crossover strategy can be used across multiple asset classes, including stocks, commodities, forex, and cryptocurrencies. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool for traders in different markets.
Cons:
-
Lagging Indicator:
One of the main drawbacks of the 200-day MA crossover strategy is that it’s a lagging indicator. Since it’s based on historical data, the signals often occur after a trend has already started, meaning traders may miss the early part of the move.
-
False Signals in Sideways Markets:
In markets that are moving sideways or exhibiting choppy price action, the 200-day MA crossover strategy can generate false signals. This is especially problematic in low-volatility environments, where prices fluctuate within a narrow range without establishing a clear trend.
- Limited Responsiveness to Short-Term Movements:
The 200-day MA is designed to capture long-term trends, which means it’s not very responsive to short-term price changes. This makes it less suitable for traders who focus on short-term price movements or who need to react quickly to sudden market changes.
-
Delayed Entries and Exits:
Because the 200-day MA crossover signals occur after a trend has begun, traders may enter or exit trades later than they would with other, more responsive strategies. This delay can reduce potential profits and increase the risk of entering trades near the end of a trend.
-
Not Always Effective in All Market Conditions:
The strategy is most effective in trending markets but can be less reliable in ranging or volatile markets. Traders need to be cautious and aware of the overall market conditions when using the 200-day MA crossover strategy.
-
Enhancing the 200-Day MA Crossover Strategy
While the 200-day MA crossover strategy is simple and effective, it can be enhanced by incorporating other technical indicators and tools to improve accuracy and reduce false signals. Here are a few ways to optimize the strategy:
-
Combine with Momentum Indicators
To filter out false signals and confirm the strength of a trend, traders often combine moving average crossovers with momentum indicators such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD).
– RSI: The RSI measures the speed and change of price movements and can help identify overbought or oversold conditions. By combining the RSI with the 200-day MA crossover, traders can get a better sense of whether the market is likely to continue its current trend or reverse course.
– MACD: The MACD indicator tracks the relationship between two moving averages (typically the 12-day and 26-day MAs) and can be used to identify changes in momentum. When combined with the 200-day MA crossover, the MACD can help confirm whether a trend is gaining or losing strength.
-
Support and Resistance Levels
Incorporating support and resistance levels can provide additional context for the 200-day MA crossover signals. For example, if a golden cross occurs near a key support level, it may be a stronger buy signal than if it occurs in the middle of a price range. Similarly, a death cross near a significant resistance level can add weight to the bearish signal.
Support and resistance levels can help traders determine whether the market has enough momentum to sustain a trend, making the crossover signals more reliable.
-
Use Multiple Time Frames
To gain a more comprehensive view of the market, traders can apply the 200-day MA crossover strategy across multiple time frames. For instance, they might use the daily chart to identify long-term trends and the 4-hour or hourly chart to fine-tune their entries and exits. This approach allows traders to align shorter-term signals with the broader trend, increasing the likelihood of success.
-
Backtesting and Paper Trading
Before applying the 200-day MA crossover strategy in live trading, it’s essential to backtest it using historical data. Backtesting allows traders to see how the strategy would have performed under different market conditions and identify any weaknesses or areas for improvement.
Additionally, paper trading—trading with virtual money—can help traders practice the strategy in real-time without risking actual capital. This allows them to refine their approach and gain confidence before trading with real money.
Real-World Examples of the 200-Day MA Crossover Strategy
To illustrate the effectiveness of the 200-day MA crossover strategy, let’s look at a few real-world examples of how it has been applied in the stock market.
Example 1: S&P 500 Golden Cross in 2019
In early 2019, the S&P 500 experienced a golden cross when the 50-day MA crossed above the 200-day MA. This signal came after a significant correction in late 2018, and the golden cross indicated that the market was entering a new uptrend. Traders who acted on this signal would have captured a substantial portion of the S&P 500’s subsequent rally, which continued for several months.
Example 2: Apple’s Death Cross in 2020
In March 2020, amid the global COVID-19 pandemic, Apple’s stock experienced a death cross when its 50-day MA crossed below the 200-day MA. This signal came during a period of extreme market volatility, and the death cross indicated that Apple’s stock was likely to continue its downward trajectory. Traders who acted on this signal would have been able to exit their positions before the stock declined further.
Example 3: Bitcoin’s Golden Cross in 2021
The 200-day MA crossover strategy is not limited to traditional assets like stocks. In September 2021, Bitcoin experienced a golden cross when its 50-day MA crossed above the 200-day MA. This bullish signal suggested that Bitcoin was entering a new upward trend, and traders who followed this signal would have been able to capture a significant portion of Bitcoin’s rally in the months that followed.
Conclusion
The 200-day moving average crossover strategy is a powerful and versatile tool for identifying long-term trends in the market. Its simplicity, strong signals, and long-term focus make it a popular choice among traders and investors alike. However, like any trading strategy, it has its drawbacks, particularly in choppy or sideways markets.
To get the most out of the 200-day MA crossover strategy, traders should consider combining it with other technical indicators, such as momentum indicators or support and resistance levels, to improve accuracy and reduce false signals. Additionally, using multiple time frames and backtesting the strategy can help traders refine their approach and increase their chances of success.
Whether you’re a long-term investor or a short-term trader looking to capitalize on major market trends, the 200-day MA crossover strategy can be a valuable addition to your trading toolkit. By understanding its strengths and weaknesses and applying it with discipline, you can use this strategy to make more informed trading decisions and improve your overall performance in the markets.