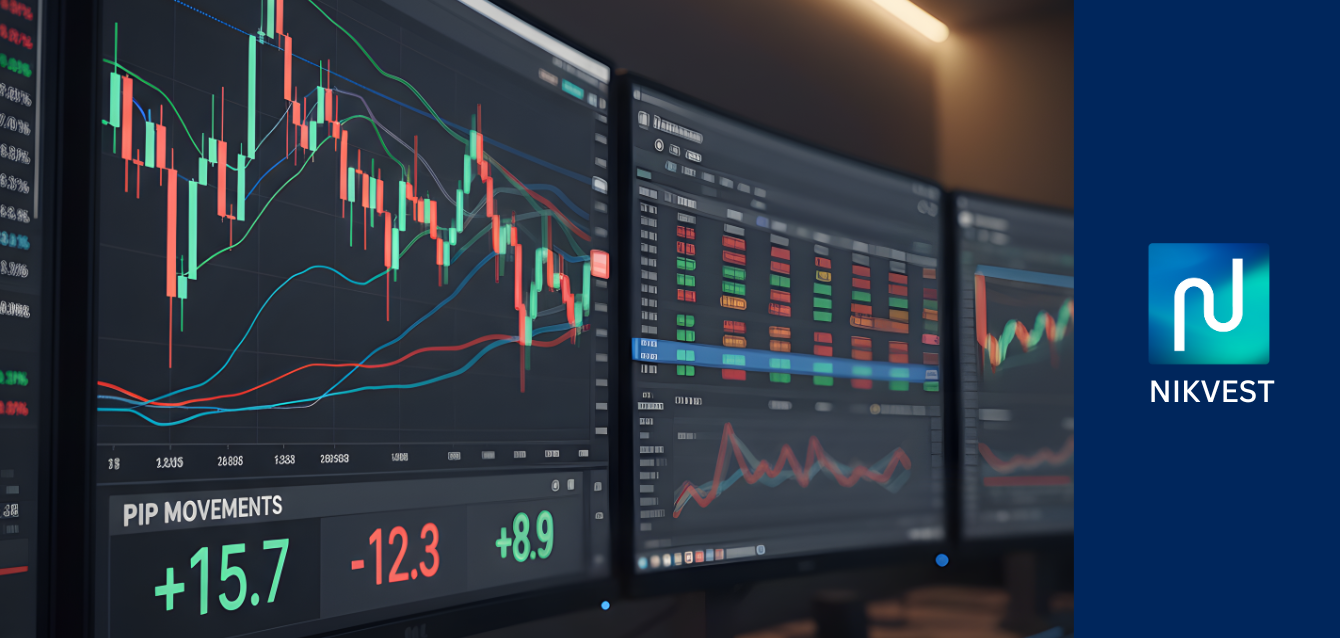
Welcome to the definitive guide on Forex pips. Whether you’re just starting your journey in the foreign exchange market or you’re an experienced trader looking to refine your understanding, mastering the concept of the pip is non-negotiable. Pips are the lifeblood of forex trading; they are the fundamental unit of measurement that quantifies your profits and losses, dictates your risk, and ultimately shapes your entire trading strategy. Without a rock-solid grasp of pips, navigating the world’s largest financial market is like sailing without a compass.
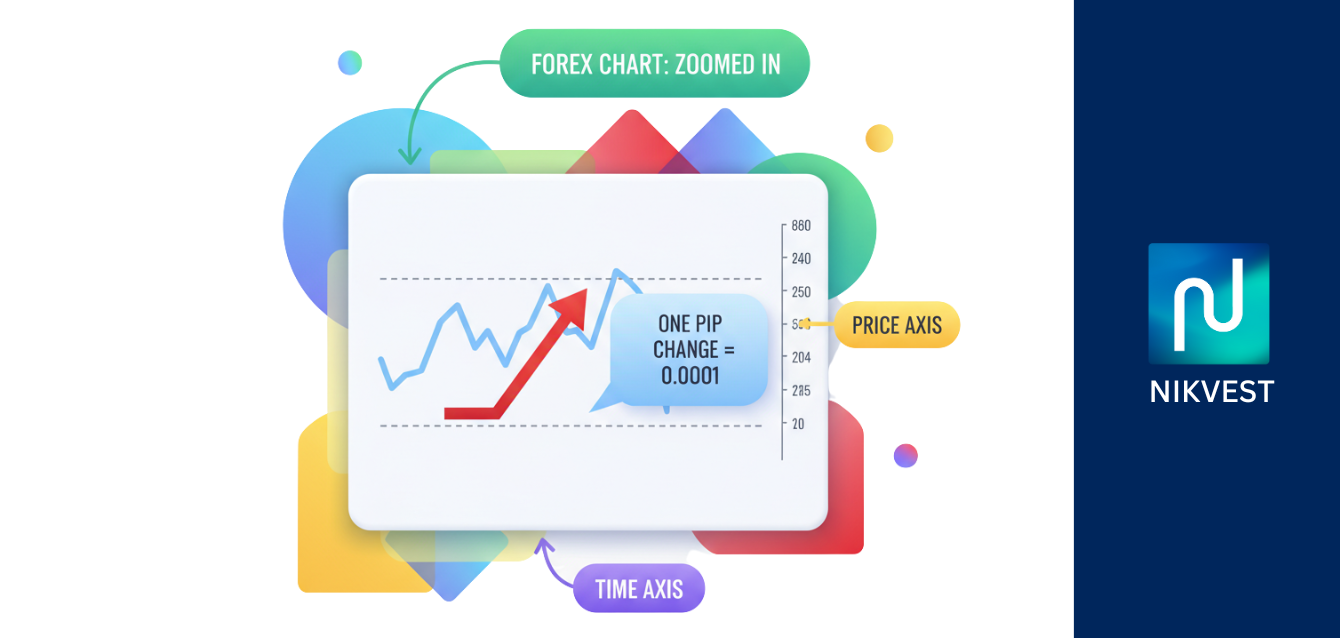
So, what exactly is a pip? The term “pip” is an acronym for “Percentage in Point” or “Price Interest Point.” It represents the smallest whole unit change in the exchange rate of a currency pair. For most pairs, it’s the fourth decimal place, but for Japanese Yen (JPY) pairs, it’s the second. Understanding this tiny unit of measurement is the first step toward understanding the mechanics of profit and loss in forex. Every tick up or down on a forex chart translates into a change in pips, which, when combined with your position size (lot size), determines the monetary value of that movement.
This article is designed to be your ultimate resource for everything related to Forex pips. We will go far beyond a simple definition, exploring the intricate relationship between pips, leverage, and lot size and pips. You will learn not just the theory but the practical application. We will delve deep into pip calculation, how to determine pip value, and how to measure profit and loss in pips. This comprehensive guide breaks down the concept into 25 detailed sections, each packed with real-world examples, step-by-step guidance, and practical tips suitable for traders at all levels. From forex trading basics to advanced risk management strategies centered around pips, this is the only guide you’ll ever need.
Article Roadmap: Your Journey to Mastering Forex Pips
- Section 1: What is a Pip? The Foundational Unit of Forex Trading
- Section 2: The History and Evolution of the Pip
- Section 3: Pips vs. Pipettes (Fractional Pips): Understanding the Fifth Decimal
- Section 4: How to Read Forex Quotes and Identify the Pip
- Section 5: The Core of Profitability: Manual Pip Calculation Explained
- Section 6: Calculating Pip Value: The Monetary Worth of a Pip
- Section 7: The Critical Link: Lot Size and Pips Explained
- Section 8: Pip Value Calculation for Standard, Mini, and Micro Lots
- Section 9: The Role of the Quote Currency in Determining Pip Value
- Section 10: Special Cases: Pip Calculation for Japanese Yen (JPY) Pairs
- Section 11: Calculating Profit and Loss in Pips: A Trader’s Scorecard
- Section 12: Using Pips to Set Stop-Loss Orders Effectively
- Section 13: Using Pips to Set Take-Profit Targets Strategically
- Section 14: The Risk-to-Reward Ratio: A Pip-Based Perspective
- Section 15: Pips and Leverage: Magnifying Gains and Losses
- Section 16: Volatility and Pips: How Market Conditions Affect Pip Movement
- Section 17: Average Daily Range (ADR) and Pips: Setting Realistic Expectations
- Section 18: Pip Differences Across Major, Minor, and Exotic Currency Pairs
- Section 19: Pips in Other Financial Instruments: Indices and Commodities
- Section 20: Automated Pip Calculators and Trading Tools
- Section 21: The Psychology of Thinking in Pips, Not Money
- Section 22: Advanced Strategy: Pip-Based Position Sizing
- Section 23: Scalping, Day Trading, and Swing Trading: A Pip-Centric View
- Section 24: Common Mistakes Traders Make with Forex Pips
- Section 25: The Future of the Pip: Will It Remain Relevant?
Section 1: What is a Pip? The Foundational Unit of Forex Trading
At its core, a pip in forex is the smallest standardized unit of change in value between two currencies. It is the fundamental building block for measuring how much an exchange rate has moved. Think of it like a single “point” of movement. When you hear traders say they “made 50 pips” on a trade, they are describing the distance the price moved in their favor.
For most currency pairs, such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, or AUD/USD, a pip is equivalent to a move in the fourth decimal place.
- Example: If the EUR/USD exchange rate moves from $1.0755 to $1.0756, that is a one-pip move.
This standardized measurement allows traders worldwide to communicate price movement universally, regardless of their account currency or the size of their trade. It creates a common language for discussing market performance. The concept of Forex pips is central to nearly every aspect of trading, from analyzing charts to managing risk. Understanding how to count them is the very first step in forex trading basics.
Why is this small unit so important? Because in the forex market, where massive volumes of currency are traded, even these tiny fractional changes can translate into significant profits or losses. The actual monetary value of a pip is determined by the trade size, also known as the lot size. A one-pip move on a small trade might be worth only a few cents, but on a large institutional trade, it could be worth thousands of dollars. This direct relationship between lot size and pips is what makes understanding them so crucial for managing your capital.
In summary, the pip is your ruler for the forex market. It measures the distance price travels, and this distance, when multiplied by your stake (lot size), determines your financial outcome.
Section 2: The History and Evolution of the Pip
The concept of the pip predates the era of modern, high-speed electronic trading. In the pre-internet age, forex quotes were not delivered with the lightning speed and precision we see today. Price changes were less frequent, and the market moved in larger, more discernible increments. The term “pip” emerged as a convenient shorthand to describe these minimum price fluctuations.
Originally, forex quotes were often provided with only four decimal places for most pairs (and two for JPY pairs). Therefore, the last decimal place was the smallest unit of movement, and this “Percentage in Point” became the standard. It simplified communication between brokers and traders in a bustling, over-the-phone trading environment. A broker could quote a price change as “up 10 pips” instead of reading out the full, cumbersome exchange rate.
The advent of electronic trading platforms and increased liquidity in the late 20th and early 21st centuries brought greater price transparency and competition among brokers. This technological leap forward led to the introduction of fractional pips, or pipettes. Brokers could now offer tighter spreads and quote prices with an additional decimal place—the fifth for most pairs and the third for JPY pairs.
This evolution from a four-digit to a five-digit pricing system marked a significant shift. While it allowed for more precise pricing and often lower transaction costs (spreads), it also introduced a potential point of confusion for new traders. However, the fundamental role of the pip as the primary unit of measurement has remained unchanged. The vast majority of experienced traders, trading algorithms, and analytical tools still refer to the fourth decimal place as the standard pip. The fractional pip, or pipette, represents one-tenth of a pip and provides a more granular view of price movement. Understanding this history helps contextualize why Forex pips are structured the way they are and why the fourth decimal place holds such significance.
Section 3: Pips vs. Pipettes (Fractional Pips): Understanding the Fifth Decimal
As technology advanced, forex brokers began offering more precise pricing, which led to the introduction of the pipette, or fractional pip. A pipette is equal to one-tenth of a standard pip.
On a modern trading platform, you will typically see currency quotes with five decimal places (or three for JPY pairs).
- Standard Pip: The fourth decimal place.
- Pipette: The fifth decimal place.
Let’s look at a EUR/USD quote: $1.07552
- The number 5 in the fourth decimal place is the pip.
- The small number 2 in the fifth decimal place is the pipette.
If the price moves from to , it has moved up by one full pip (). If it moves from to , it has moved up by one pipette ().
Why Does This Distinction Matter?
- Spread Calculation: Spreads, the difference between the bid and ask price, are often quoted in pips but can be fractional. A spread of 0.7 pips is actually 7 pipettes. This precision is crucial for scalpers and high-frequency traders where every fraction of a pip counts.
- Trading Platform Clarity: It’s essential to know how your trading platform displays price changes. Some platforms might show profit and loss in terms of full pips, while others might show it in pipettes (often referred to as ‘points’). A platform showing a profit of “200 points” might mean a gain of 20.0 pips. Always check your platform’s settings or documentation.
- Avoiding Confusion: For beginners, this can be a common source of error. When calculating your risk or potential profit, always be certain whether you are working with pips or pipettes. As a rule of thumb, unless specified otherwise, the standard unit of measurement in forex discussions, strategies, and analysis is the standard pip.
While pipettes provide more granularity, the Forex pip remains the king. For strategic planning, like setting a 50-pip stop-loss or a 100-pip take-profit, traders almost exclusively think in terms of standard pips.
Section 4: How to Read Forex Quotes and Identify the Pip
Reading a forex quote is a fundamental skill, and identifying the pip within that quote is the next logical step. A currency quote always shows two currencies: the base currency and the quote currency.
Quote Structure: BASE / QUOTE
- Base Currency: The first currency in the pair (e.g., EUR in EUR/USD). It is the currency you are buying or selling. It always has a value of 1.
- Quote Currency: The second currency in the pair (e.g., USD in EUR/USD). It is the currency used to price the base currency.
Let’s take the quote GBP/USD = 1.25468.
This means: 1 British Pound (GBP) is worth 1.25468 US Dollars (USD).
Identifying the Pip in Different Pairs:
- For most pairs (EUR/USD, GBP/USD, AUD/USD, etc.): The pip is the fourth decimal place.
- In 1.25468, the number 6 is the pip digit.
- The number 8 is the pipette.
- A move from to is a 1-pip increase.
- For Japanese Yen (JPY) pairs (USD/JPY, EUR/JPY, GBP/JPY, etc.): The pip is the second decimal place. This is the main exception to the rule.
- In a USD/JPY quote of 148.753, the number 5 is the pip digit.
- The number 3 is the pipette.
- A move from to is a 1-pip increase.
Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners:
- Look at the currency pair. Identify if JPY is the quote currency.
- If it’s NOT a JPY pair: Find the fourth digit after the decimal point. That’s your pip. The fifth digit is the pipette.
- If it IS a JPY pair: Find the second digit after the decimal point. That’s your pip. The third digit is the pipette.
Mastering this simple identification process is crucial. It’s the starting point for every pip calculation and the foundation for understanding profit and loss in pips.
Section 5: The Core of Profitability: Manual Pip Calculation Explained
While most trading platforms automatically calculate your profit and loss, knowing how to perform a manual pip calculation is essential for a deeper understanding of your trades and for planning them away from your screen. It demystifies the process and puts you in full control.
The calculation itself is straightforward subtraction.
Formula for Pip Movement:
- For a Long (Buy) trade:
Pips = Exit Price - Entry Price - For a Short (Sell) trade:
Pips = Entry Price - Exit Price
Let’s walk through some examples.
Example 1: Long Trade on EUR/USD
Imagine you believe the Euro will strengthen against the US Dollar.
- You buy EUR/USD at an entry price of .
- The price moves up, and you close the trade at an exit price of .
To calculate the pips gained: Pips = 1.07750 - 1.07250 = 0.00500
Since for EUR/USD one pip is , we can determine the number of pips by dividing the difference by the pip value in decimals: Number of Pips = 0.00500 / 0.00010 = 50 pips
You made a profit of 50 pips.
Example 2: Short Trade on USD/JPY
Now, let’s say you predict the US Dollar will weaken against the Japanese Yen.
- You sell USD/JPY at an entry price of .
- The price moves down as you predicted, and you close the trade at an exit price of .
To calculate the pips gained: Pips = 148.500 - 148.100 = 0.400
For JPY pairs, one pip is . So, we divide the difference by : Number of Pips = 0.400 / 0.010 = 40 pips
You made a profit of 40 pips.
What if the Trade Goes Against You?
Let’s revisit the first example, but this time it’s a losing trade.
- You buy EUR/USD at .
- The price falls, and you close the trade at .
Pips = 1.07150 - 1.07250 = -0.00100 Number of Pips = -0.00100 / 0.00010 = -10 pips
You incurred a loss of 10 pips.
This manual pip calculation is a foundational skill. It allows you to quickly assess the performance of past trades from your history and to mentally track the progress of active trades. It forms the basis for the next crucial step: determining the monetary pip value.
Section 6: Calculating Pip Value: The Monetary Worth of a Pip
Knowing you’ve made or lost a certain number of Forex pips is only half the story. The critical question is: what is that move worth in cold, hard cash? This is where pip value comes in. The pip value tells you the monetary gain or loss for every one-pip move in the exchange rate.
The pip value is influenced by three key factors:
- The currency pair being traded.
- The size of your trade (your lot size).
- The exchange rate of the quote currency against your account currency.
The General Formula for Pip Value:
The formula looks like this:
Pip Value = (Pip in Decimal Form / Exchange Rate) * Lot Size
Let’s break this down with a standard lot size of 100,000 units.
- Pip in Decimal Form: This is for most pairs and for JPY pairs.
- Exchange Rate: This is the current rate of the currency pair if the quote currency is different from your account currency.
- Lot Size: The number of base currency units you are trading.
Scenario 1: Account Currency is the Same as the Quote Currency
This is the simplest scenario. Let’s say your account is funded in USD, and you are trading EUR/USD. The quote currency is USD, matching your account currency.
- Currency Pair: EUR/USD
- Lot Size: 1 Standard Lot (100,000 units of EUR)
- Pip in Decimal Form:
The calculation is straightforward: Pip Value = 0.0001 * 100,000 = $10
In this case, for a standard lot of EUR/USD, the pip value is exactly $10. Every time the price moves one pip, you make or lose $10.
Scenario 2: Account Currency is Different from the Quote Currency
This requires an extra step. Let’s say your account is funded in EUR, and you are trading USD/CAD. The quote currency is CAD.
- Currency Pair: USD/CAD
- Lot Size: 1 Standard Lot (100,000 units of USD)
- Pip in Decimal Form:
- Current Exchange Rate (USD/CAD): Let’s assume it’s .
- Current Exchange Rate (EUR/USD): Let’s assume it’s (needed to convert back to your account currency).
Step 1: Calculate the pip value in the quote currency (CAD). Pip Value in CAD = (0.0001 / 1.35000) * 100,000 = 7.4074 CAD
So, one pip move is worth approximately 7.41 Canadian Dollars.
Step 2: Convert the pip value to your account currency (EUR). To do this, we need the EUR/CAD rate. If we don’t have it, we can use EUR/USD and USD/CAD. The conversion would be: Pip Value in EUR = Pip Value in CAD / (EUR/CAD exchange rate) Assuming EUR/CAD is (): Pip Value in EUR = 7.4074 / 1.4580 = €5.08
As you can see, the pip value is not always a fixed number like $10. It fluctuates based on the pair you trade and the currency of your account. Fortunately, you don’t need to perform this complex pip calculation manually every time; brokers and online calculators do it for you. However, understanding the mechanics is what separates a novice from an informed trader.
Section 7: The Critical Link: Lot Size and Pips Explained
The relationship between lot size and pips is arguably one of the most important concepts in risk management and forex trading basics. A pip is a measurement of distance, but the lot size determines the financial weight or value of that distance.
Think of it this way: Driving one mile is a fixed distance. But the cost (in fuel, time, and vehicle wear) of driving that mile is vastly different if you’re in a tiny smart car versus a massive freight truck.
In forex:
- Pips are the miles (distance).
- Lot Size is the vehicle (your financial weight).
Standard Lot Sizes in Forex:
The term “lot” refers to the size of a trade. There are three primary lot sizes you must know:
- Standard Lot:
- Units: 100,000 units of the base currency.
- Value: A 1-pip move is typically worth about $10 (if USD is the quote currency).
- Who uses it? Professional and institutional traders, or well-capitalized retail traders. Trading with standard lots means profits and losses accumulate very quickly.
- Mini Lot:
- Units: 10,000 units of the base currency (one-tenth of a standard lot).
- Value: A 1-pip move is typically worth about $1.
- Who uses it? Intermediate retail traders who have graduated from micro lots but are not yet ready for the risk of a standard lot.
- Micro Lot:
- Units: 1,000 units of the base currency (one-tenth of a mini lot).
- Value: A 1-pip move is typically worth about $0.10 (10 cents).
- Who uses it? Beginners are strongly advised to start with micro lots. The small pip value allows you to learn the market dynamics without risking significant capital.
The Impact of Lot Size on a Trade:
Let’s assume you have a trading strategy that aims for a 50-pip profit with a 25-pip stop-loss on the EUR/USD pair.
- Trading a Micro Lot (0.01 lots):
- Potential Profit: 50 pips * $0.10/pip = $5
- Potential Loss: 25 pips * $0.10/pip = $2.50
- Trading a Mini Lot (0.1 lots):
- Potential Profit: 50 pips * $1/pip = $50
- Potential Loss: 25 pips * $1/pip = $25
- Trading a Standard Lot (1.0 lots):
- Potential Profit: 50 pips * $10/pip = $500
- Potential Loss: 25 pips * $10/pip = $250
The number of Forex pips moved is identical in all three scenarios. The strategy is the same. The chart looks the same. But the financial and psychological impact is worlds apart. This example powerfully illustrates that managing your lot size is just as important, if not more important, than predicting the direction of the market. Your lot size is your primary risk control lever.
Section 8: Pip Value Calculation for Standard, Mini, and Micro Lots
Let’s dive deeper into the practical pip calculation for different lot sizes. Understanding this allows you to know exactly how much money is at risk before you even enter a trade. We will use currency pairs where the USD is the quote currency for simplicity, as this results in fixed, easy-to-remember pip values.
The Base Case: USD as the Quote Currency
Examples: EUR/USD, GBP/USD, AUD/USD, NZD/USD. In these pairs, the pip value is fixed and directly proportional to the lot size.
- Standard Lot (100,000 units or 1.0 lot):
- Calculation:
0.0001 (pip) * 100,000 (units) = $10.00 - Pip Value = $10 per pip.
- Calculation:
- Mini Lot (10,000 units or 0.1 lot):
- Calculation:
0.0001 (pip) * 10,000 (units) = $1.00 - Pip Value = $1 per pip.
- Calculation:
- Micro Lot (1,000 units or 0.01 lot):
- Calculation:
0.0001 (pip) * 1,000 (units) = $0.10 - Pip Value = $0.10 per pip.
- Calculation:
- Nano Lot (100 units or 0.001 lot):
- Some brokers offer nano lots, which are even smaller.
- Calculation:
0.0001 (pip) * 100 (units) = $0.01 - Pip Value = $0.01 per pip.
Table: Pip Value Summary (USD as Quote Currency)
Practical Application and Step-by-Step Guidance:
Let’s say you’re a beginner with a $500 account. You want to risk no more than 2% of your account on a single trade, which is $10. Your strategy involves a 20-pip stop-loss on GBP/USD.
- Determine Max Risk in Dollars:
$500 * 2% = $10 - Determine Stop-Loss in Pips: 20 pips
- Calculate Required Pip Value:
Max Risk ($) / Stop-Loss (pips) = $10 / 20 pips = $0.50 per pip - Choose the Right Lot Size:
- A micro lot ($0.10/pip) is too small.
- A mini lot ($1.00/pip) is too large (
20 pips * $1 = $20 risk). - You need a lot size that gives you a $0.50 pip value.
- Calculate the Exact Lot Size:
- Since 1 mini lot (0.10) gives a $1 pip value, you need half of that.
- Your ideal lot size is 0.05 lots (5 micro lots).
- Let’s check the math:
0.05 lots = 5,000 units.0.0001 * 5,000 = $0.50. - Risk check:
20 pips * $0.50/pip = $10. Perfect.
This process, which connects your risk tolerance (in percent) to your stop-loss (in pips) to determine your position size (in lots), is a cornerstone of professional money management. The relationship between lot size and pips is at the heart of this calculation.
Section 9: The Role of the Quote Currency in Determining Pip Value
As we touched on in Section 6, the pip value calculation becomes more complex when your account currency is different from the quote currency. The quote currency (the second currency in a pair) is what determines the currency in which the pip value is denominated.
Let’s clarify this with distinct scenarios. Assume your trading account is funded in US Dollars (USD).
Scenario 1: USD is the Quote Currency (e.g., EUR/USD, GBP/USD)
- As we’ve established, the pip value is fixed. For a standard lot, it’s $10. This is because the profit or loss from a pip move is already in USD, so no conversion is needed.
Scenario 2: USD is the Base Currency (e.g., USD/JPY, USD/CAD, USD/CHF)
- Here, the quote currency is JPY, CAD, or CHF. This means the pip value is first calculated in that currency and then must be converted back to your account currency (USD).
Example: Pip Value Calculation for USD/CAD
- Account Currency: USD
- Trade: Long 1 Standard Lot of USD/CAD
- Lot Size: 100,000 USD
- Current USD/CAD Rate: 1.3550
- Pip in Decimal Form: 0.0001 CAD
Step 1: Calculate Pip Value in the Quote Currency (CAD) Pip Value (CAD) = 0.0001 * 100,000 = 10 CAD Notice this is always 10 units of the quote currency for a standard lot.
Step 2: Convert Pip Value to Account Currency (USD) To convert 10 CAD to USD, we need to divide by the USD/CAD exchange rate. Pip Value (USD) = Pip Value (CAD) / USD/CAD Rate Pip Value (USD) = 10 CAD / 1.3550 = $7.38
So, for this trade, each pip of movement is worth $7.38, not $10. As the USD/CAD exchange rate fluctuates, this pip value will also change. If USD/CAD rises to 1.4000, the pip value would fall to $10 / 1.4000 = $7.14.
Scenario 3: USD is Not in the Pair (Cross-Currency Pairs, e.g., EUR/GBP, AUD/NZD, GBP/JPY)
- This is the most complex scenario, requiring a two-step conversion.
Example: Pip Value Calculation for EUR/GBP
- Account Currency: USD
- Trade: Short 1 Standard Lot of EUR/GBP
- Lot Size: 100,000 EUR
- Current EUR/GBP Rate: 0.8500
- Pip in Decimal Form: 0.0001 GBP
Step 1: Calculate Pip Value in the Quote Currency (GBP) Pip Value (GBP) = 0.0001 * 100,000 = 10 GBP
Step 2: Convert Pip Value to Account Currency (USD) Now we need to convert 10 GBP to USD. To do this, we need the current GBP/USD exchange rate.
- Let’s assume the GBP/USD rate is 1.2500.
Pip Value (USD) = Pip Value (GBP) * GBP/USD RatePip Value (USD) = 10 GBP * 1.2500 = $12.50
In this case, one pip of movement on EUR/GBP is worth $12.50. This is significantly different from the standard $10 value.
Key Takeaway: The quote currency dictates the denomination of the pip value. You must always perform a conversion if the quote currency is not your account’s base currency. Modern trading platforms do this for you in real-time, but understanding the underlying math is crucial for risk management and for appreciating why your P/L on a 10-pip move can vary so much between different pairs.
Section 10: Special Cases: Pip Calculation for Japanese Yen (JPY) Pairs
Japanese Yen (JPY) pairs are the primary exception to the standard four-decimal-place rule for Forex pips. This is because the value of a single Yen is very small compared to other major currencies like the Dollar, Euro, or Pound. As a result, forex quotes involving the JPY are only taken to two or three decimal places.
The JPY Pip Rule:
- For any currency pair where JPY is the quote currency (e.g., USD/JPY, EUR/JPY, GBP/JPY), a pip is the second decimal place ().
- A pipette is the third decimal place ().
Example of a USD/JPY Quote:
Let’s say the quote for USD/JPY is 148.753.
- The digit 5 (in the second decimal place) represents the pip.
- The digit 3 (in the third decimal place) represents the pipette.
If the rate moves from to , that is a one-pip increase. A move from to would be a 100-pip increase.
Pip Value Calculation for JPY Pairs
The process for calculating the pip value is the same as for other pairs, but we use as the pip in decimal form. Let’s calculate the pip value for USD/JPY for a trader with a USD account.
- Account Currency: USD
- Trade: Long 1 Standard Lot of USD/JPY
- Lot Size: 100,000 USD
- Current USD/JPY Rate: 148.75
- Pip in Decimal Form: 0.01 JPY
Step 1: Calculate Pip Value in the Quote Currency (JPY) This step is slightly different. The formula is Pip Value = Lot Size * Pip in Decimal Form. Pip Value (JPY) = 100,000 * 0.01 = 1,000 JPY So, for a standard lot of any JPY pair, one pip of movement is always worth 1,000 JPY.
Step 2: Convert Pip Value to Account Currency (USD) To convert 1,000 JPY to USD, we must divide by the USD/JPY exchange rate. Pip Value (USD) = Pip Value (JPY) / USD/JPY Rate Pip Value (USD) = 1,000 JPY / 148.75 = $6.72
So, at the current rate, one pip on USD/JPY is worth $6.72 for a standard lot.
Why is this important? Traders must be aware that the pip value for JPY pairs is not static.
- As the USD/JPY rate increases (Yen gets weaker), the USD value of each pip decreases.
- As the USD/JPY rate decreases (Yen gets stronger), the USD value of each pip increases.
This dynamic pip value needs to be factored into your risk management. A 20-pip stop-loss on USD/JPY will represent a different dollar risk amount depending on the current exchange rate, unlike a 20-pip stop on EUR/USD, which is always a fixed dollar amount (assuming a USD account). This is a subtle but critical detail for precise position sizing.
Section 11: Calculating Profit and Loss in Pips: A Trader’s Scorecard
One of the most powerful psychological and analytical shifts a trader can make is to measure their performance primarily in pips, not in their account currency. Calculating your profit and loss in pips provides a standardized, objective measure of your trading skill, independent of your account size or the amount you risk per trade.
Why Measure in Pips?
- Objectivity: A 50-pip gain is a 50-pip gain, whether it was on a micro lot (worth $5) or a standard lot (worth $500). It measures your ability to read the market, not the size of your wallet.
- Performance Tracking: It allows you to analyze your strategy’s effectiveness over time. If your strategy averages a +25 pip profit per winning trade and a -15 pip loss per losing trade, you know you have a positive expectancy, regardless of lot size.
- Psychological Detachment: Focusing on pips helps to disconnect your emotions from the fluctuating dollar value of your trade. Chasing a “50-pip target” feels more strategic and less emotional than chasing a “$500 target.” This is a key aspect of trading psychology.
- Scalability: As your account grows, you can increase your lot size, but your pip-based targets remain the same. A strategy that nets you 200 pips a month can be scaled up from earning $20 (on micro lots) to $200 (on mini lots) to $2,000 (on standard lots) without changing the core strategy itself.
How to Calculate Total Profit and Loss in Pips
The calculation is a simple aggregation of your individual trade results.
Step-by-Step Example:
Let’s say you took three trades in a day:
- Trade 1 (Long EUR/USD): Entered at 1.0750, exited at 1.0790.
Pip Gain = 1.0790 - 1.0750 = 0.0040Result = +40 pips
- Trade 2 (Short GBP/USD): Entered at 1.2560, exited at 1.2585 (Stop-Loss hit).
Pip Loss = 1.2560 - 1.2585 = -0.0025Result = -25 pips
- Trade 3 (Long USD/JPY): Entered at 148.10, exited at 148.70.
Pip Gain = 148.70 - 148.10 = 0.60Result = +60 pips
Daily P/L in Pips: Total Pips = (+40) + (-25) + (+60) = +75 pips
Your net result for the day is a profit of 75 pips. This is your performance scorecard. The dollar value of these 75 pips will depend on the lot sizes you used for each trade and the specific pip value for each pair at the time. But the raw skill measure—capturing 75 pips from the market—is constant. Keeping a trading journal where you meticulously log your profit and loss in pips is one of the most effective habits a developing trader can adopt.
Section 12: Using Pips to Set Stop-Loss Orders Effectively
A stop-loss order is an instruction to your broker to close a losing trade once the price reaches a certain predefined level. It is your primary defense mechanism against catastrophic losses. The most logical and effective way to determine your stop-loss placement is by using pips.
Setting a stop-loss based on a random dollar amount (e.g., “I’ll close if I’m down $100”) is a recipe for disaster. Why? Because a $100 loss could be a small 10-pip move on a standard lot or a massive 100-pip move on a mini lot. The dollar amount is arbitrary; the pip distance is technical and strategic.
Strategies for Setting Stop-Losses Based on Pips:
- Technical Level Placement (The Professional Method):
- This is the most widely used and respected method. You place your stop-loss at a logical price level on the chart that would invalidate your trading idea.
- For a long (buy) trade: Place the stop-loss a certain number of pips below a key support level, a recent swing low, or a significant moving average.
- For a short (sell) trade: Place the stop-loss a certain number of pips above a key resistance level, a recent swing high, or a moving average.
- Example: You want to buy EUR/USD, and you identify a strong support level at 1.0700. You don’t place your stop exactly at 1.0700, as price might briefly dip below to “hunt for stops.” Instead, you give it a buffer. You might set your stop-loss 15 pips below this level, at 1.0685. Your risk is now clearly defined in pips.
- Volatility-Based Placement (Using ATR):
- The Average True Range (ATR) indicator measures market volatility. When volatility is high, price swings are larger, so you need a wider stop-loss. When volatility is low, you can use a tighter stop.
- Method: Check the ATR value on your chart (e.g., 14-period ATR). If the ATR is 20 pips, you might set your stop-loss at a multiple of that value, such as 1.5x or 2x the ATR, away from your entry price. This adapts your risk to the current market conditions.
- Fixed Pip Stop-Loss (Common for Scalping):
- Scalpers, who trade for very small, quick profits, often use a fixed-pip stop-loss. For example, a scalper might decide that they will exit any trade that goes against them by 10 pips, no matter what.
- This method is less technically sound but can be effective for very short-term strategies where speed is essential and deep analysis of chart structure is not feasible for every entry.
The Golden Rule: First, determine your stop-loss placement in pips based on your technical analysis. THEN, calculate the appropriate lot size to ensure that pip distance equates to a dollar amount you are comfortable risking (e.g., 1-2% of your account).
Never do it the other way around (choosing your lot size first and then seeing where the stop-loss lands). Your analysis of the market should dictate your risk in pips, and your risk management rules should dictate your position size.
Section 13: Using Pips to Set Take-Profit Targets Strategically
Just as a stop-loss protects you from excessive losses, a take-profit order secures your gains by automatically closing a winning trade when the price reaches a specified target. Setting these targets is an art and a science, and it is most effectively done by measuring the distance in Forex pips.
A well-placed take-profit target helps you overcome two of the most destructive trading emotions: greed and fear. Greed might tempt you to hold onto a winning trade for too long, only to watch it reverse and turn into a loser. Fear might cause you to snatch a small profit too early, missing out on a much larger potential move. A predefined, pip-based target imposes discipline.
Strategies for Setting Take-Profit Targets Based on Pips:
- Support and Resistance Levels:
- This is the inverse of setting a stop-loss. If you are in a long (buy) trade, your take-profit target could be set a few pips below the next significant resistance level. Why below? Because the price might reach just shy of the level before reversing.
- If you are in a short (sell) trade, your target could be set a few pips above the next major support level.
- Example: You are short GBP/USD from 1.2600. You identify a strong historical support zone starting at 1.2520. A prudent take-profit target might be 1.2525. This gives you a target of
1.2600 - 1.2525 = 75 pips.
- Risk-to-Reward Ratio:
- This is a highly disciplined approach. Before entering a trade, you decide on an acceptable risk-to-reward ratio. Common ratios are 1:1.5, 1:2, or 1:3.
- Method: First, you determine your stop-loss in pips. Let’s say your technical analysis leads you to a 30-pip stop-loss.
- For a 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio, your take-profit target would be
30 pips * 2 = 60 pipsaway from your entry. - For a 1:3 risk-to-reward ratio, your target would be
30 pips * 3 = 90 pips.
- For a 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio, your take-profit target would be
- This ensures that your winning trades are significantly larger than your losing trades, meaning you can be profitable even if you win less than 50% of your trades.
- Fibonacci Extension Levels:
- For traders who use Fibonacci analysis, extension levels (like 127.2%, 161.8%, etc.) are excellent, non-obvious places to set take-profit targets. These levels project where a price wave might end after a retracement.
- Trailing Stops:
- A trailing stop is a dynamic take-profit and stop-loss hybrid. You set it to “trail” the price by a specific number of pips.
- Example: You go long EUR/USD and set a 25-pip trailing stop. If the price moves in your favor by 40 pips, your stop-loss automatically moves up to lock in
40 - 25 = 15 pipsof profit. If the price continues to rise, the stop follows it, always maintaining that 25-pip distance. If the price then reverses and falls by 25 pips, your trade is closed, securing the profit you’ve locked in. This allows you to ride a strong trend while still protecting your gains.
Ultimately, your method for setting take-profit targets in pips should be a core component of your written trading plan. It provides a logical exit strategy, which is just as important as your entry strategy.
Section 14: The Risk-to-Reward Ratio: A Pip-Based Perspective
The Risk-to-Reward (R/R) ratio is a cornerstone concept in professional trading and money management. It quantifies how much potential profit you expect to make for every unit of risk you are willing to take. The most effective way to calculate and apply this ratio is by using pips.
The Formula: Risk-to-Reward Ratio = (Distance to Take-Profit in Pips) / (Distance to Stop-Loss in Pips)
Why is R/R So Important?
The R/R ratio is intimately linked to your win rate (the percentage of your trades that are profitable). Together, they determine if your trading strategy has a positive expectancy—that is, if it’s likely to be profitable over the long term.
Consider two traders:
- Trader A: Has a high win rate (70%) but a poor R/R ratio. They risk 30 pips to make 10 pips (a 1:0.33 R/R).
- Trader B: Has a low win rate (40%) but a great R/R ratio. They risk 20 pips to make 60 pips (a 1:3 R/R).
Let’s see how they fare over 10 trades:
- Trader A’s Results:
- 7 wins * 10 pips = +70 pips
- 3 losses * 30 pips = -90 pips
- Net Result = -20 pips (Losing money despite winning 70% of the time!)
- Trader B’s Results:
- 4 wins * 60 pips = +240 pips
- 6 losses * 20 pips = -120 pips
- Net Result = +120 pips (Making good money despite losing 60% of the time!)
This powerful example shows that a high win rate means nothing without a favorable risk-to-reward ratio. You do not need to be right all the time to be a profitable trader; you just need to ensure your winners are significantly larger than your losers.
Applying R/R Using Pips: A Practical Walkthrough
- Analyze the Chart: Before placing a trade, identify your ideal entry point, a logical stop-loss level (below support/above resistance), and a logical take-profit target (below resistance/above support).
- Measure the Distances in Pips:
- Let’s say you want to buy USD/CAD at 1.3500.
- Your logical stop-loss is at 1.3470 (a 30-pip risk).
- Your logical take-profit target is at 1.3590 (a 90-pip potential reward).
- Calculate the R/R Ratio:
R/R = 90 pips / 30 pips = 3- This is a 1:3 Risk-to-Reward Ratio.
- Make a Decision: Many professional traders will not even consider taking a trade unless it offers a minimum R/R ratio, often 1:1.5 or 1:2. Since this trade offers 1:3, it is a high-quality setup from a risk management perspective. If the potential reward was only 45 pips (1:1.5), you might still take it. If it was only 15 pips (1:0.5), you should almost certainly pass on the trade, no matter how confident you feel about the direction.
Thinking in terms of pip-based risk-to-reward ratios transforms trading from a gambling exercise into a strategic, business-like endeavor. It forces you to be selective and to only risk your capital on setups that have a sound mathematical edge.
Section 15: Pips and Leverage: Magnifying Gains and Losses
Leverage is a powerful tool in forex trading that allows you to control a large position size with a relatively small amount of capital in your account. It’s often described as a “double-edged sword” because it magnifies both your potential profits and your potential losses. The concept of Forex pips is central to understanding how leverage works in practice.
Leverage is expressed as a ratio, such as 50:1, 100:1, or even 500:1. A 100:1 leverage ratio means that for every $1 in your account (the margin), you can control $100 in the market.
- Example: To open a standard lot position (100,000 units) of EUR/USD without leverage, you would need $100,000 in your account. With 100:1 leverage, you only need to put up
1/100of that amount as margin.Margin Required = $100,000 / 100 = $1,000
Leverage is what makes forex accessible to retail traders with smaller account sizes. It allows them to trade meaningful position sizes.
How Leverage Interacts with Pips
Leverage does not change the pip value. A one-pip move on a standard lot of EUR/USD is still worth $10, regardless of whether you used 10:1 or 500:1 leverage.
So, what does leverage do? It allows you to trade a larger lot size than you otherwise could, which in turn increases the monetary impact of each pip’s movement.
Let’s illustrate with a trader who has a $2,000 account balance.
- Scenario 1: No Leverage (1:1)
- The largest position this trader can open is
$2,000. This is equivalent to 2 micro lots (2,000 units). - The pip value for 2 micro lots is approximately $0.20 per pip.
- A 50-pip profit would be
$0.20 * 50 = $10. - A 50-pip loss would be
-$10. - The movements are very small relative to the account size.
- The largest position this trader can open is
- Scenario 2: High Leverage (e.g., 200:1)
- This leverage allows the trader to control a much larger position. Let’s say the trader decides to open a mini lot (10,000 units), which requires only
$10,000 / 200 = $50in margin. This is well within their $2,000 account. - The pip value for a mini lot is approximately $1 per pip.
- A 50-pip profit is now
$1 * 50 = $50. - A 50-pip loss is now
-$50.
- This leverage allows the trader to control a much larger position. Let’s say the trader decides to open a mini lot (10,000 units), which requires only
- Scenario 3: Extremely High Leverage (Danger Zone)
- The same trader, tempted by high leverage, decides to open a standard lot (100,000 units). The margin required is
$100,000 / 200 = $500. Again, well within their $2,000 account. - The pip value for a standard lot is $10 per pip.
- A 50-pip profit is now
$10 * 50 = $500(a 25% account gain!). - A 50-pip loss is now
-$500(a 25% account loss!). - What if the price moves against them by 200 pips? The loss would be
$10 * 200 = $2,000, wiping out their entire account. This is known as a margin call.
- The same trader, tempted by high leverage, decides to open a standard lot (100,000 units). The margin required is
Key Takeaway: Leverage does not make the market riskier; it allows the trader to take on more risk. The risk comes from choosing a lot size that is too large for your account. The movement of Forex pips is the constant. Leverage is the magnifier that determines whether that constant movement results in a small ripple or a tidal wave in your account equity. Respect leverage, and always control your risk by choosing a sensible lot size based on a pip-defined stop-loss.
Section 16: Volatility and Pips: How Market Conditions Affect Pip Movement
Volatility is a measure of the magnitude and speed of price fluctuations in a financial market. In forex, volatility is directly observed through the movement of pips. A highly volatile market is one that moves a large number of pips in a short amount of time. A low-volatility market moves very few pips and tends to trade sideways.
Understanding the relationship between volatility and pips is crucial for adapting your trading strategy to different market environments.
How Volatility is Measured and Observed:
- Eyeballing the Chart: The simplest way is to look at the length of the candlesticks. Long candles indicate high volatility (large pip movements within that period), while short, stubby candles (like Dojis) indicate low volatility.
- Average True Range (ATR): As mentioned earlier, the ATR is a technical indicator that provides a numerical value for volatility. An ATR reading of 50 on the daily chart for EUR/USD means the pair has moved an average of 50 pips per day over the last ‘N’ periods (typically 14).
- Bollinger Bands: This indicator consists of a moving average and two bands plotted above and below it. When the bands widen, it signals increasing volatility. When they contract (a “squeeze”), it signals decreasing volatility, often preceding a significant breakout.
How Volatility Affects Your Pip-Based Strategy:
- High Volatility (e.g., during major news releases, market openings):
- Pros: Opportunity for large and rapid pip gains. Trends can be strong and clear.
- Cons: Requires wider stop-losses in pips to avoid being “stopped out” by random noise. The market can be erratic and unpredictable. Spreads may widen, increasing transaction costs.
- Strategy Adjustment: You might need to reduce your lot size to accommodate the wider pip-stop, keeping your dollar risk constant. Take-profit targets in pips can be set further away.
- Low Volatility (e.g., during the Asian session, summer months, before holidays):
- Pros: Markets are calmer and more predictable. Good for range-trading strategies (buying at support, selling at resistance).
- Cons: Pip movements are small, meaning profit potential is limited. Breakout strategies will fail frequently as the price lacks momentum.
- Strategy Adjustment: You might use tighter pip-stops and more modest take-profit targets. Scalping for 5-10 pips can be more effective than swing trading for 100 pips.
Practical Example:
Imagine your strategy is to trade breakouts with a 20-pip stop-loss and a 60-pip take-profit.
- In a low-volatility market, the price might break out by 15 pips and then reverse, hitting your 20-pip stop. The momentum isn’t there to reach your 60-pip target. Your strategy will likely fail.
- In a high-volatility market, a breakout might surge 100 pips in a matter of minutes. Your 60-pip target is easily hit. However, the initial “whipsaw” around the breakout point might be 30 pips wide, so your tight 20-pip stop would have been hit before the move even started.
Conclusion: A successful trader is a chameleon, adapting their strategy to the environment. This means adjusting your pip-based parameters—your stop-loss distance, your take-profit distance, and your expectations for how many Forex pipsa pair is likely to move—based on the current level of market volatility.
Section 17: Average Daily Range (ADR) and Pips: Setting Realistic Expectations
The Average Daily Range (ADR) is a simple yet powerful indicator that measures the average distance, in pips, that a currency pair moves from its high to its low in a single day. It’s typically calculated over a period of 5, 10, or 14 days.
Understanding a pair’s ADR is essential for setting realistic and achievable trading goals. It helps answer the critical question: “Is my take-profit target reasonable for today’s market?”
How to Use ADR in Your Trading:
Most trading platforms have an ADR indicator you can add to your charts. It will display a value in pips.
Let’s say the 14-day ADR for GBP/JPY (a historically volatile pair) is 150 pips. And the 14-day ADR for EUR/CHF (a historically low-volatility pair) is 45 pips.
This information is invaluable for strategy planning.
1. Setting Take-Profit Targets:
- If you are day trading GBP/JPY and the pair has already moved 130 pips since the day’s open, setting a take-profit target another 50 pips away is statistically unlikely to be hit on the same day. The pair has likely exhausted most of its daily potential. A more realistic target might be just 20-30 pips further.
- Conversely, if you are trading EUR/CHF and are looking for a 100-pip profit, you need to understand that this is more than double the pair’s average daily movement. Such a target would only be suitable for a swing trade held over several days, not a day trade.
2. Setting Stop-Losses:
- If the ADR for a pair is 100 pips, using a very tight 10-pip stop-loss might be inappropriate. The normal “noise” and intraday swings could easily be 20-30 pips, meaning you would likely get stopped out before your trade has a chance to play out. Your stop-loss distance in pips should be proportional to the pair’s typical volatility, which the ADR helps quantify.
3. Choosing Which Pairs to Trade:
- A scalper or a day trader who needs volatility to make a profit would be drawn to pairs with a high ADR, like GBP/JPY or GBP/USD.
- A trader who prefers slower, more predictable movements might prefer pairs with a lower ADR, like EUR/CHF or AUD/NZD.
Practical Walkthrough:
- You are a day trader looking at EUR/USD. You check the ADR indicator, and it shows a value of 75 pips.
- The trading day has been open for several hours, and the range from the day’s high to the day’s low so far is 60 pips.
- You see a potential long entry.
- Analysis: The pair has already completed
60/75 = 80%of its average daily movement. While it could have an exceptionally volatile day and extend further, the odds are that the remaining potential is limited. - Decision: You might decide to aim for a smaller take-profit target of 15-20 pips, or you might pass on the trade altogether, judging that the best part of the daily move is already over.
The ADR provides crucial context. It grounds your pip-based targets in statistical reality, preventing you from chasing unrealistic profits or using stop-losses that are inappropriate for a pair’s typical behavior.
Section 18: Pip Differences Across Major, Minor, and Exotic Currency Pairs
The forex market is categorized into three main types of currency pairs: majors, minors (or crosses), and exotics. The characteristics of these pairs, particularly their volatility and liquidity, have a direct impact on their pip behavior.
1. Major Pairs
- Definition: Seven pairs that involve the US Dollar (USD) and another major world currency. They are: EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, USD/CHF, AUD/USD, NZD/USD, and USD/CAD.
- Characteristics:
- High Liquidity: They are the most traded pairs, meaning there are always lots of buyers and sellers.
- Low Spreads: Due to high competition and liquidity, the cost of trading (the spread) is very low, often less than one pip.
- Predictable Pip Movement: While they can be volatile, their movements are often smoother and more influenced by major global economic news. Their ADRs are generally moderate.
- Example: EUR/USD is the king of forex, known for its massive volume and tight spreads. It’s an ideal pair for beginners learning about Forex pips.
2. Minor Pairs (Cross-Currency Pairs)
- Definition: Pairs that do not involve the US Dollar but consist of two other major currencies. Examples: EUR/GBP, EUR/JPY, GBP/AUD, CAD/JPY.
- Characteristics:
- Good Liquidity: Still highly liquid, but less so than the majors.
- Slightly Wider Spreads: Spreads are typically wider than for majors, ranging from 1 to 5 pips depending on the pair and broker.
- Potentially Higher Volatility: Some crosses, particularly those involving GBP or JPY (like GBP/JPY, known as “The Dragon” or “Widowmaker”), can have very high ADRs and move hundreds of pips in a single day.
- Example: GBP/JPY can offer huge profit potential due to its volatility, but it also carries significantly higher risk. The stop-loss required in pips will be much larger than for EUR/USD.
3. Exotic Pairs
- Definition: A major currency paired with the currency of an emerging or smaller economy. Examples: USD/TRY (Turkish Lira), EUR/ZAR (South African Rand), USD/MXN (Mexican Peso).
- Characteristics:
- Low Liquidity: Far fewer market participants, leading to less smooth price action.
- Very Wide Spreads: Spreads can be extremely wide, sometimes 50 pips or more. This is a significant transaction cost.
- Extreme Volatility and Gapping: These pairs are highly sensitive to local economic and political events. They can move thousands of pips in a short time and are prone to “gapping” (when the price jumps from one level to another with no trading in between), which can cause your stop-loss to be executed at a much worse price than intended (slippage).
- Example: During a political crisis in Turkey, the USD/TRY could move 5,000 pips in a week. While this sounds attractive, the risk is immense. The pip value for these pairs is often very small, but the sheer number of pips moved can lead to huge profits or devastating losses.
Trader’s Guide:
- Beginners: Stick to the major pairs. Their low spreads and predictable behavior provide the best learning environment.
- Intermediate Traders: Can explore the minor pairs to find more trading opportunities, but must be prepared to handle wider spreads and increased volatility by adjusting their pip-based risk parameters.
- Advanced Traders: Only experienced and well-capitalized traders should consider exotic pairs. The risks are substantial and require a deep understanding of the specific economies involved.
Section 19: Pips in Other Financial Instruments: Indices and Commodities
While the term “pip” is most famous in the forex market, the underlying concept of a standardized minimum price movement is used across many other leveraged financial instruments, often available through the same forex brokers. However, the terminology and value of these movements can differ significantly.
1. Stock Indices (e.g., S&P 500, DAX 40, FTSE 100)
- Unit of Measurement: Instead of “pips,” the movement in indices is measured in “points” or “ticks.”
- Value: A one-point move in an index represents a change of 1.00 in the index’s price. For example, a move in the S&P 500 (US500) from 4500.00 to 4501.00 is a 1-point move.
- Contract Specifications: The monetary value of a one-point move is determined by the broker’s contract specifications for that particular index CFD (Contract for Difference). For many brokers, a 1.0 lot trade on the US500 might mean that a 1-point move is worth $10 (similar to a standard lot pip in forex). However, this can vary wildly between brokers and indices. It is absolutely crucial to check the contract details before trading.
- Example: You buy 1.0 lot of the DAX 40 (GER40) at 15500. The broker’s contract specifies that 1 point is worth €1 per lot. The index rallies to 15550. Your profit is
50 points * €1/point = €50.
2. Commodities (e.g., Gold, Oil, Silver)
- Gold (XAU/USD):
- Measurement: Gold is priced in USD per troy ounce. A move from $1950.00 to $1951.00 is a $1 move. Many traders refer to the first decimal place ($0.10) as a “pip” and the second decimal place ($0.01) as a “tick.”
- Value: For a standard 1.0 lot (representing 100 ounces of gold), a $1 move in the price typically results in a $100 profit or loss. Therefore, a $0.10 “pip” move is worth $10.
- Crude Oil (WTI/Brent):
- Measurement: Oil is priced in USD per barrel. The smallest move is typically $0.01, which is called a “tick.”
- Value: A standard 1.0 lot in oil CFDs often represents 1,000 barrels. The value of a tick is calculated as
0.01 * 1,000 = $10. So, for every one-cent move in the price of oil, a standard lot trader makes or loses $10. A full $1 move (e.g., from $80.00 to $81.00) would be worth$10/tick * 100 ticks = $1,000.
Key Takeaway: The principle of measuring profit and loss based on standardized price movements is universal. However, do not assume a “pip” in forex is the same as a “point” in the DAX or a “tick” in oil. Each instrument has its own unique contract specifications. Before trading anything other than forex, you must take the time to read and understand exactly what a minimum price fluctuation means in terms of monetary value for the lot size you are trading. This is a critical step in risk management.
Section 20: Automated Pip Calculators and Trading Tools
While understanding manual pip calculation is essential for a solid foundation, in day-to-day trading, using automated tools can save time, reduce errors, and allow you to make decisions more quickly. The modern trading landscape is filled with excellent tools designed to handle the number-crunching for you.
Types of Pip-Related Tools:
- Pip Value Calculators:
- These are widely available online and often integrated into broker websites.
- Function: You simply input the currency pair, your trade size (in lots or units), and your account currency. The calculator instantly tells you the exact value of one pip.
- Why use it? It’s perfect for quickly checking the pip value of cross-currency or exotic pairs without having to look up multiple exchange rates and do manual conversions. This is a must-have tool for anyone trading a diverse range of pairs.
- Position Size Calculators:
- This is arguably the most important risk management tool a trader can use.
- Function: You input your account balance, the percentage of your account you wish to risk (e.g., 1% or 2%), your stop-loss distance in pips, and the currency pair. The calculator then tells you the exact lot size you should use to ensure your risk on that trade does not exceed your predefined limit.
- Example:
- Account Balance: $5,000
- Risk %: 2% (Max loss = $100)
- Pair: GBP/JPY
- Stop-Loss: 40 pips
- The calculator will perform the complex pip value calculation for GBP/JPY in your account currency and then determine that to risk $100 with a 40-pip stop, you need to use, for example, 0.38 lots.
- In-Platform Tools (Indicators and Expert Advisors):
- Many trading platforms like MetaTrader (MT4/MT5) and TradingView have custom indicators and tools that display pip-related information directly on your chart.
- Measuring Tool: Most platforms have a “crosshair” or “ruler” tool. You can click and drag it between two price points on your chart, and it will instantly show you the distance in pips, the number of bars, and the percentage change. This is invaluable for quickly measuring potential stop-loss and take-profit distances.
- P/L Displays: Your trading terminal will show your open positions with a running profit/loss column. Many can be configured to show this P/L in pips as well as your account currency, helping you focus on performance rather than just money.
Best Practices for Using Calculators:
- Bookmark Your Favorites: Find a reliable and easy-to-use Pip Value and Position Size calculator and keep it bookmarked for quick access.
- Use Before Every Trade: Make using the position size calculator a non-negotiable part of your pre-trade routine. It instills discipline and ensures you never risk more than you intend to.
- Understand the Inputs: Be sure you know whether the calculator requires your stop-loss in pips or pipettes. A 40-pip stop is very different from a 40-pipette (4 pips) stop.
These tools don’t replace the need to understand Forex pips, but they are powerful allies that handle the tedious calculations, freeing you up to focus on what truly matters: analyzing the market and executing your strategy.
Section 21: The Psychology of Thinking in Pips, Not Money
One of the biggest hurdles for traders to overcome is the emotional rollercoaster caused by watching their account balance fluctuate with every market tick. A winning trade brings euphoria; a losing trade brings despair. This emotional attachment to money leads to poor decision-making, such as cutting winners short out of fear or holding losers too long in the desperate hope they’ll turn around.
A powerful antidote to this destructive emotional cycle is to train yourself to think in pips, not money.
Why Thinking in Pips is a Psychological Superpower:
- Objectivity and Abstraction:
- Pips are an abstract, objective unit of measurement. Focusing on capturing a “+40 pip” gain is a strategic, game-like objective. It feels like scoring points. Focusing on making “+$400” is directly tied to what that money can buy or what it feels like to lose it. By abstracting the goal into pips, you create a psychological buffer between your trading decisions and your real-world financial anxieties.
- Consistency Across a Scalable Career:
- Your trading strategy should be consistent, whether you’re trading a $500 account or a $500,000 account. A 20-pip stop-loss should be a 20-pip stop-loss. If you think in money, your behavior will change as your account size grows. A -$20 loss on a $500 account feels manageable. But a -$20,000 loss on a $500,000 account (the same 20-pip move with a larger lot size) can be terrifying, even though it’s the same proportional risk (4%). This fear can cause you to abandon a perfectly good strategy. Thinking in pips keeps your actions consistent regardless of the stakes.
- Focus on the Process, Not the Outcome:
- Successful trading is about flawless execution of a well-tested strategy over and over again. When you focus on your profit and loss in pips, you are measuring how well you executed your process. Did you identify a good setup? Did you place your stop correctly? Did you manage the trade according to your plan? The pip result tells you this. The dollar result is simply an outcome of that process multiplied by your chosen risk. Focusing on the process leads to long-term success; focusing on the dollar outcome leads to short-term emotional trading.
How to Cultivate a Pip-Focused Mindset:
- Journal in Pips: Keep a detailed trading journal, but make the primary performance metric your net gain/loss in pips for the day, week, and month. Relegate the dollar amount to a secondary column.
- Set Pip-Based Goals: Instead of “I want to make $1,000 this month,” set a goal like “I want to net +200 pips this month.” This goal is entirely within your control as it depends on your trading skill, whereas the dollar amount also depends on your account size.
- Customize Your Platform: If possible, change the settings on your trading platform to display your running P/L in pips instead of or alongside the monetary value.
- Use a Position Size Calculator Religiously: By systematically calculating your lot size based on a fixed percentage risk and a pip-based stop, you make the dollar risk a constant. This helps you to stop worrying about the money and focus on the technicals of the trade—the pips.
Making this mental shift is one of an intermediate trader’s most important steps toward becoming a professional. It builds discipline, emotional resilience, and a focus on what truly matters: a consistent, well-executed trading process.
Section 22: Advanced Strategy: Pip-Based Position Sizing
We’ve discussed using a position size calculator, which is a fundamental risk management technique. Now let’s explore a more advanced, dynamic approach: pip-based position sizing that adapts to market volatility.
The core idea is that the amount of risk you take should be constant (e.g., 1% of your account), but the way that risk is distributed can change.
The Standard Model (Fixed Fractional): Risk a fixed percentage of your account on every trade. This is the classic model we’ve discussed.
Position Size = (Account Equity * Risk %) / (Stop-Loss in Pips * Pip Value)
The Advanced Model (Volatility-Adjusted Position Sizing):
This model recognizes that a 30-pip stop-loss in a low-volatility environment is very different from a 30-pip stop-loss in a high-volatility environment. The advanced model uses volatility (often measured by the ATR) to determine the stop-loss distance, and then calculates the position size based on that.
Step-by-Step Volatility-Adjusted Sizing:
- Define Your Max Risk in Dollars:
- Account Equity: $10,000
- Risk Percentage: 1.5%
- Max Dollar Risk per Trade:
$10,000 * 0.015 = $150
- Determine Volatility-Based Stop-Loss in Pips:
- You are looking at a long trade on GBP/USD.
- You check the 14-period ATR on the H1 chart. The current value is 18 pips. This tells you the average range of an hourly candle is 18 pips.
- You decide that a reasonable stop-loss should be able to withstand at least the average amount of noise, so you set your stop-loss at a multiple of the ATR. A common multiple is 2x.
- Your Stop-Loss in Pips =
18 pips (ATR) * 2 = 36 pips.
- Calculate the Required Position Size:
- You know your max dollar risk is $150.
- You know your stop-loss distance is 36 pips.
- First, find the required dollar value per pip:
$150 / 36 pips = $4.17 per pip. - Next, determine the lot size needed to achieve this pip value for GBP/USD (where the pip value is standard).
- 1 mini lot (0.10) = $1/pip
- 1 standard lot (1.00) = $10/pip
- Lot Size =
$4.17 / $10 = 0.417standard lots. So, you would trade 0.42 lots (or 4 mini lots and 2 micro lots).
Why is this advanced?
Let’s say one week later, the market is much quieter. The ATR on GBP/USD has dropped to just 9 pips.
- Your new stop-loss would be
9 pips * 2 = 18 pips. - Required dollar value per pip =
$150 / 18 pips = $8.33 per pip. - New Lot Size =
$8.33 / $10 = 0.833standard lots. You would trade 0.83 lots.
Comparison:
- High Volatility: Wider pip stop (36 pips), smaller position size (0.42 lots).
- Low Volatility: Tighter pip stop (18 pips), larger position size (0.83 lots).
This dynamic approach ensures your dollar risk is always the same ($150), but it adapts your position size to the market’s rhythm. You take smaller positions when the market is “shouting” (high volatility) and larger positions when it is “whispering” (low volatility). This can significantly improve a strategy’s performance by reducing the impact of random noise in volatile markets and maximizing potential in quieter, trending markets. It is a hallmark of a sophisticated, risk-aware trader.
Section 23: Scalping, Day Trading, and Swing Trading: A Pip-Centric View
Different trading styles have vastly different objectives when it comes to capturing Forex pips. The number of pips targeted per trade is a key factor that distinguishes a scalper from a day trader, and a day trader from a swing trader.
1. Scalping
- Timeframe: Very short-term (seconds to minutes). Typically uses 1-minute to 5-minute charts.
- Pip Objective: To capture very small pip movements, often between 5 to 15 pips per trade.
- Strategy: Scalpers enter and exit the market very frequently throughout the day, aiming to profit from small price fluctuations. Because the pip target is so small, they must use larger lot sizes to make the profit meaningful. This also means they need extremely tight spreads and fast execution.
- Pip-Centric View: For a scalper, every single pipette matters. A spread of 0.8 pips is a significant hurdle when the target is only 7 pips. They are hyper-focused on the bid-ask spread and the immediate price action. Their stop-losses are also very tight, often in the 5-10 pip range.
2. Day Trading
- Timeframe: Short-term (minutes to hours). Typically uses 15-minute to 1-hour charts.
- Pip Objective: To capture intraday moves, typically aiming for 20 to 75 pips per trade.
- Strategy: Day traders open and close all their positions within a single trading day, avoiding overnight risk. They might take one to five high-quality trades per day, looking for moves between key intraday support and resistance levels.
- Pip-Centric View: A day trader is focused on the pair’s Average Daily Range (ADR). They need to know how many pips a pair is likely to move in a day to set realistic targets. They use pip-based stop-losses (e.g., 20-30 pips) and take-profits that align with a favorable risk-to-reward ratio (e.g., aiming for 40 pips with a 20-pip stop).
3. Swing Trading
- Timeframe: Medium-term (days to weeks). Typically uses 4-hour, daily, and weekly charts.
- Pip Objective: To capture larger market “swings,” targeting 100 to 500+ pips per trade.
- Strategy: Swing traders identify a major trend on a higher timeframe and hold their positions for several days or even weeks to capitalize on the bulk of that move. They are less concerned with short-term market noise.
- Pip-Centric View: For a swing trader, the daily pip fluctuations are just noise. Their stop-losses are much wider, often 50 to 150 pips, to accommodate daily volatility and avoid being stopped out prematurely. Their primary focus is on the larger pip potential. A 2-pip spread is almost irrelevant when the profit target is 300 pips. They think in terms of large pip distances between major weekly support and resistance zones.
Table: Pip Objectives by Trading Style
Your personality and schedule will largely determine which style suits you best. But regardless of your choice, your strategy will be defined by your pip-based goals for both risk (stop-loss) and reward (take-profit).
Section 24: Common Mistakes Traders Make with Forex Pips
Understanding the concept of Forex pips is one thing; applying it correctly under pressure is another. Many trading errors, especially among beginners, stem from a misunderstanding or misapplication of pip-based principles. Here are some of the most common mistakes to avoid.
1. Ignoring Pip Value Differences
- The Mistake: Assuming a 50-pip stop-loss represents the same dollar risk on EUR/USD as it does on GBP/JPY or XAU/USD (Gold).
- The Consequence: The trader inadvertently takes on massive risk when trading pairs with a high pip value or commodities, leading to unexpectedly large losses. A $500 loss might occur when they were only expecting to risk $250.
- The Solution: Always use a pip value calculator or a position size calculator before trading any new pair. Understand that pip values are dynamic for non-USD-quoted pairs.
2. Setting Arbitrary Dollar-Based Stops
- The Mistake: Setting a stop-loss based on a comfortable dollar amount, like “$100 loss,” instead of a technical level on the chart.
- The Consequence: The stop-loss is placed in a random, meaningless location on the chart. It might be too close and get hit by normal market noise, or too far away, representing poor risk-to-reward.
- The Solution: Always determine your stop-loss placement based on technical analysis (support/resistance, swing points, ATR) first. This defines your risk in pips. Then, adjust your lot size so that this pip distance equals your desired dollar risk.
3. Confusing Pips and Pipettes
- The Mistake: Entering “20” into a platform’s stop-loss field, thinking it’s 20 pips, when the platform actually interprets it as 20 pipettes (only 2.0 pips).
- The Consequence: The trade is stopped out almost instantly by the spread or the smallest of market fluctuations, leading to frustration and unnecessary losses.
- The Solution: Know your platform. Check whether its order entry module works in pips or points/pipettes. Do a test trade on a demo account to be certain.
4. Widening a Stop-Loss (A Cardinal Sin)
- The Mistake: A trade goes against the trader and approaches their 30-pip stop-loss. In fear of taking the loss, they move the stop further away to 50 pips, hoping the price will reverse.
- The Consequence: This is how small, manageable losses turn into account-destroying disasters. It invalidates the original risk-to-reward ratio and is a purely emotional decision.
- The Solution: Treat your initial stop-loss as sacred. Once it is set, based on sound technical reasoning, never widen it. If it gets hit, accept the loss as a business expense and move on to the next opportunity.
5. Not Factoring in the Spread
- The Mistake: Placing a buy stop order or a take-profit for a short trade at exactly the same price as a key resistance level.
- The Consequence: For a buy order to be triggered or a short to be closed, the ask price must reach that level. Since the ask price is always higher than the bid price (which is what you see on the chart), the price may appear to hit the level on the chart, but the order never fills because the spread wasn’t overcome.
- The Solution: Always account for the spread. Add a few pips to your entry for buy stops, and give your take-profits a buffer of a few pips below resistance (for longs) or above support (for shorts).
Avoiding these common pitfalls related to Forex pips is a massive step towards building the discipline and precision required for long-term trading success.
Section 25: The Future of the Pip: Will It Remain Relevant?
In an era of high-frequency trading, algorithmic systems, and ever-increasing market precision, is the humble pip, a concept from the pre-digital age, at risk of becoming obsolete? The answer, for the foreseeable future, is a resounding no.
While the financial world evolves, the fundamental reasons for the pip’s existence remain as strong as ever.
1. The Need for Standardization
- The global forex market involves millions of participants, from central banks to individual retail traders, all speaking different languages and using different currencies. The pip provides a simple, universal language for price movement. A “50-pip move” is understood instantly by a trader in Tokyo, London, and New York. No other system of measurement has achieved this level of universal adoption.
2. The Human Element
- Despite the rise of algorithms, a vast portion of the market is still driven by human traders who think, analyze, and communicate in terms of pips. Key psychological levels are often round numbers (e.g., 1.1000 on EUR/USD), and strategic targets are set in round pip figures (e.g., a 100-pip stop or a 200-pip target). This human behavior, centered around pips, creates self-fulfilling prophecies in the market. As long as humans are involved, pips will remain the mental framework for trading.
3. The Foundation of Risk Management
- The entire architecture of modern retail forex risk management is built upon the pip. Position sizing models, risk-to-reward ratios, and volatility assessments all use the pip as their foundational unit. Dismantling this framework would require a complete re-education of the industry and a redesign of our most essential trading tools.
Potential Evolutions, Not Revolutions:
- Increased Granularity: The introduction of the pipette (the fifth decimal) was an evolution, not a replacement. We may see even greater precision in the future, perhaps with a sixth decimal place, as technology allows for even tighter spreads. However, the pip (the fourth decimal) will almost certainly remain the standard reference point, with any further digits being treated as fractions of it.
- Focus on Percentage Moves: In the institutional and academic worlds, large-scale currency movements are often discussed in percentage terms (e.g., “the dollar fell by 0.5% today”). This is a more accurate way to compare volatility across different assets. However, for the practical application of placing a stop-loss or a take-profit on a chart, the fixed-distance measurement of a pip remains far more intuitive and actionable for a trader.
100 pipsis an easy-to-visualize distance on a chart;0.87%is not.
Conclusion: The Forex pip is more than just a unit of measurement; it is part of the culture and language of trading. It is woven into the fabric of our charts, our strategies, and our risk management systems. While the technology around it will continue to advance, the pip’s role as the fundamental building block of forex trading is secure. Mastering it is not just learning a historical concept; it is learning the timeless language of the market itself.
Conclusion: The Pip as Your Compass in the Forex Market
We have journeyed through 25 distinct sections, deconstructing the Forex pip from every conceivable angle. We began with a simple definition—a pip as the smallest unit of price change—and expanded to show that it is, in fact, the central gear in the complex machinery of forex trading.
From the historical evolution of the pip to its modern-day fractional counterpart, the pipette, we established the foundational knowledge needed to read any forex quote with confidence. We moved from theory to practice, mastering the crucial skills of pip calculation and determining pip value, understanding that a pip’s worth is a dynamic figure shaped by the currency pair, your lot size, and your account currency.
The critical relationship between lot size and pips was a recurring theme, highlighting that while pips measure the journey, lot size determines the financial impact of that journey. This understanding forms the bedrock of all sound risk management. We saw how to apply this knowledge tactically, using pips to set technically sound stop-loss orders to protect capital and strategic take-profit orders to secure gains, all governed by the mathematical discipline of the risk-to-reward ratio.
We explored the intricate dance between pips and market forces like leverage and volatility, learning to adapt our pip-based strategies to the market’s ever-changing rhythm. Finally, we elevated the discussion from mechanics to mindset, emphasizing the psychological power of thinking in pips to foster objectivity and discipline—the hallmarks of a professional trader.
If there is one key takeaway from this exhaustive guide, it is this: a deep, multifaceted understanding of the pip is not optional; it is essential. The pip is your unit of risk, your measure of performance, and your tool for strategic planning. It is the language you use to define your edge in the market. By mastering the concepts within these 25 sections, you are no longer simply guessing or gambling. You are equipped with the knowledge to manage your trades, control your risk, and navigate the world’s largest financial market with precision, confidence, and professionalism.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a pip in forex?
A pip, which stands for “Percentage in Point” or “Price Interest Point,” is the smallest standardized unit of measurement for a change in the exchange rate of a currency pair. For most pairs like the EUR/USD, it is the fourth decimal place (e.g., ). For pairs involving the Japanese Yen (JPY), it is the second decimal place (e.g., ). Forex pips are the fundamental unit used to calculate profit and loss in pips.
How is pip value calculated?
The pip value is the monetary worth of a one-pip move. The calculation depends on the trade size (lot size) and the quote currency. For a standard lot (100,000 units) on a pair where USD is the quote currency (like EUR/USD), the calculation is simple: 100,000 * 0.0001 = $10. For other pairs, you first calculate the value in the quote currency and then convert it to your account’s base currency using the current exchange rate.
How do lot sizes affect pips?
Lot size does not affect the pip itself, but it directly determines the monetary value of each pip move. The relationship between lot size and pips is crucial for risk management.
- Standard Lot (1.00): One pip is worth about $10.
- Mini Lot (0.10): One pip is worth about $1.
- Micro Lot (0.01): One pip is worth about $0.10. A 50-pip move can result in a $500 profit/loss with a standard lot but only a $5 profit/loss with a micro lot.
Why do Forex pips matter for risk management?
Forex pips are essential for risk management because they provide an objective, technical way to define risk. Instead of using an arbitrary dollar amount, traders set their stop-loss orders based on a specific number of pips determined by technical analysis (e.g., 30 pips below a support level). They then use a position size calculator to determine the correct lot size, ensuring that this 30-pip risk corresponds to a pre-determined percentage of their account (e.g., 1%). This disciplined, pip-based approach prevents emotional decision-making and catastrophic losses.
Can beginners trade successfully by focusing on pips?
Absolutely. Focusing on Forex pips is one of the best habits a beginner can develop. It shifts the focus from the emotional pursuit of money to the strategic process of executing a trading plan. By setting goals in pips (e.g., “net 100 pips this month”) and measuring performance in pips, beginners learn to value their trading skill and process over short-term monetary outcomes. This pip-centric mindset is a foundational element of forex trading basics and builds the discipline needed for long-term success.
Resources
1. Babypips – What is a Pip in Forex Trading?
Purpose: Beginner-friendly explanation of pips and pipettes.
Intro: Babypips breaks down what a pip is, how it’s measured in different currency pairs, and why it’s crucial for managing risk and calculating profits.
https://www.babypips.com/learn/forex/what-is-a-pip
2. Investopedia – Definition of a Pip
Purpose: Clear definition with formulas and examples.
Intro: Investopedia provides a concise yet thorough explanation of pips, showing how they relate to lot sizes, leverage, and price movement in major forex pairs.
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/pip.asp
3. FXCM – Pip Calculator
Purpose: Real-time pip value calculation.
Intro: FXCM’s pip calculator helps traders instantly find the value of one pip in any currency pair — essential for accurate position sizing and risk management.
https://www.fxcm.com/tools/pip-calculator/
4. OANDA – Pip Value Calculator
Purpose: Tool to calculate pip value by pair, lot size, and account currency.
Intro: OANDA offers a free calculator that simplifies pip value estimation, making it easier to align your trade size with your risk tolerance.
https://www.oanda.com/forex-trading/analysis/pip-calculator/
5. DailyFX – Understanding Pips and Pipettes
Purpose: Educational guide with market examples.
Intro: DailyFX explains how pips are used in real market conditions and how even small pip movements can translate into significant profit or loss.
https://www.dailyfx.com/education/beginner/what-is-a-pip.html